Enfuvirtide (T20)-Based Lipopeptide Is a Potent HIV-1 Cell Fusion Inhibitor: Implications for Viral Entry and Inhibition
Ding, X., Zhang, X., Chong, H., Zhu, Y., Wei, H., Wu, X., He, J., Wang, X., He, Y.(2017) J Virol 91
- PubMed: 28659478
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00831-17
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
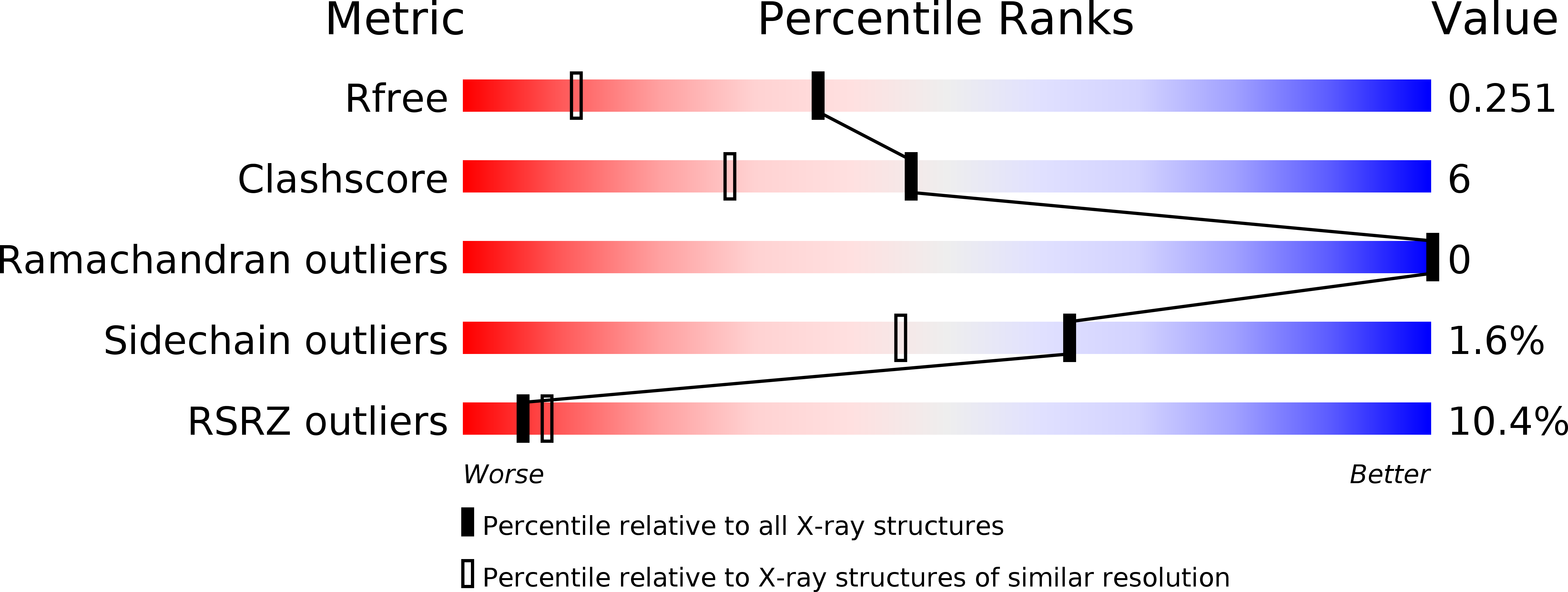
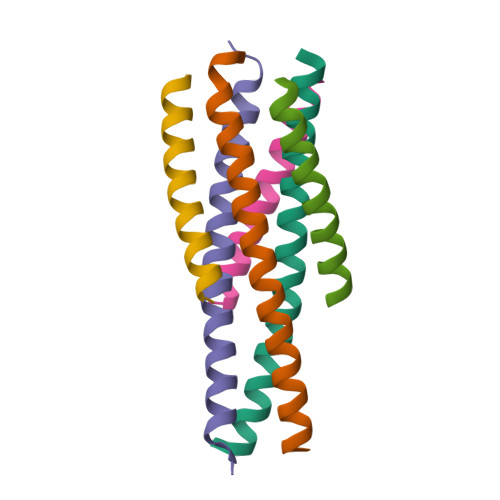
5Y14 - PubMed Abstract:
The peptide drug enfuvirtide (T20) is the only viral fusion inhibitor used in combination therapy for HIV-1 infection, but it has relatively low antiviral activity and easily induces drug resistance. Emerging studies demonstrate that lipopeptide-based fusion inhibitors, such as LP-11 and LP-19, which mainly target the gp41 pocket site, have greatly improved antiviral potency and in vivo stability. In this study, we focused on developing a T20-based lipopeptide inhibitor that lacks pocket-binding sequence and targets a different site. First, the C-terminal tryptophan-rich motif (TRM) of T20 was verified to be essential for its target binding and inhibition; then, a novel lipopeptide, termed LP-40, was created by replacing the TRM with a fatty acid group. LP-40 showed markedly enhanced binding affinity for the target site and dramatically increased inhibitory activity on HIV-1 membrane fusion, entry, and infection. Unlike LP-11 and LP-19, which required a flexible linker between the peptide sequence and the lipid moiety, addition of a linker to LP-40 sharply reduced its potency, implying different binding modes with the extended N-terminal helices of gp41. Also, interestingly, LP-40 showed more potent activity than LP-11 in inhibiting HIV-1 Env-mediated cell-cell fusion while it was less active than LP-11 in inhibiting pseudovirus entry, and the two inhibitors displayed synergistic antiviral effects. The crystal structure of LP-40 in complex with a target peptide revealed their key binding residues and motifs. Combined, our studies have not only provided a potent HIV-1 fusion inhibitor, but also revealed new insights into the mechanisms of viral inhibition. IMPORTANCE T20 is the only membrane fusion inhibitor available for treatment of viral infection; however, T20 requires high doses and has a low genetic barrier for resistance, and its inhibitory mechanism and structural basis remain unclear. Here, we report the design of LP-40, a T20-based lipopeptide inhibitor that has greatly improved anti-HIV activity and is a more potent inhibitor of cell-cell fusion than of cell-free virus infection. The binding modes of two classes of membrane-anchoring lipopeptides (LP-40 and LP-11) verify the current fusion model in which an extended prehairpin structure bridges the viral and cellular membranes, and their complementary effects suggest a vital strategy for combination therapy of HIV-1 infection. Moreover, our understanding of the mechanism of action of T20 and its derivatives benefits from the crystal structure of LP-40.
Organizational Affiliation:
MOH Key Laboratory of Systems Biology of Pathogens, Institute of Pathogen Biology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China.