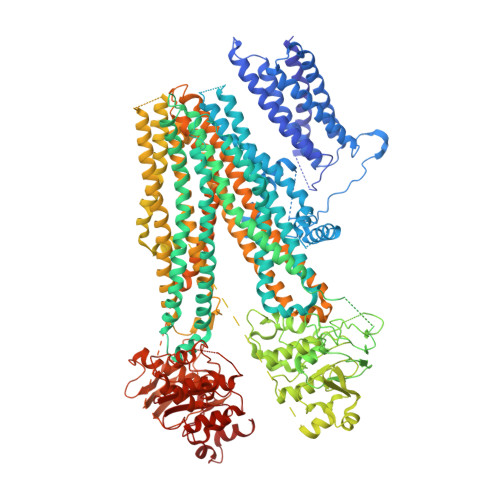
Structure of a Pancreatic ATP-Sensitive Potassium Channel
Li, N., Wu, J.X., Ding, D., Cheng, J., Gao, N., Chen, L.(2017) Cell 168: 101-110.e10
- PubMed: 28086082
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.12.028
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5WUA - PubMed Abstract:
ATP-sensitive potassium channels (K ATP ) couple intracellular ATP levels with membrane excitability. These channels play crucial roles in many essential physiological processes and have been implicated extensively in a spectrum of metabolic diseases and disorders. To gain insight into the mechanism of K ATP , we elucidated the structure of a hetero-octameric pancreatic K ATP channel in complex with a non-competitive inhibitor glibenclamide by single-particle cryoelectron microscopy to 5.6-Å resolution. The structure shows that four SUR1 regulatory subunits locate peripherally and dock onto the central Kir6.2 channel tetramer through the SUR1 TMD0-L0 fragment. Glibenclamide-bound SUR1 uses TMD0-L0 fragment to stabilize Kir6.2 channel in a closed conformation. In another structural population, a putative co-purified phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP 2 ) molecule uncouples Kir6.2 from glibenclamide-bound SUR1. These structural observations suggest a molecular mechanism for K ATP regulation by anti-diabetic sulfonylurea drugs, intracellular adenosine nucleotide concentrations, and PIP 2 lipid.
- State Key Laboratory of Membrane Biology, Institute of Molecular Medicine, Peking-Tsinghua Center for Life Sciences, Beijing Key Laboratory of Cardiometabolic Molecular Medicine, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China; School of Life Sciences, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China.
Organizational Affiliation: