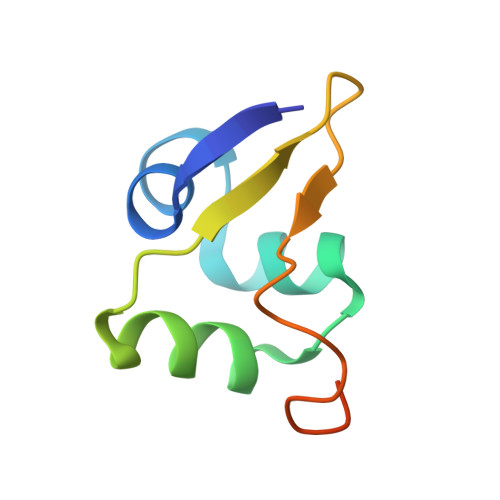
Multistep mutational transformation of a protein fold through structural intermediates.
Kumirov, V.K., Dykstra, E.M., Hall, B.M., Anderson, W.J., Szyszka, T.N., Cordes, M.H.J.(2018) Protein Sci 27: 1767-1779
- PubMed: 30051937
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.3488
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5W8Y, 5W8Z - PubMed Abstract:
New protein folds may evolve from existing folds through metamorphic evolution involving a dramatic switch in structure. To mimic pathways by which amino acid sequence changes could induce a change in fold, we designed two folded hybrids of Xfaso 1 and Pfl 6, a pair of homologous Cro protein sequences with ~40% identity but different folds (all-α vs. α + β, respectively). Each hybrid, XPH1 or XPH2, is 85% identical in sequence to its parent, Xfaso 1 or Pfl 6, respectively; 55% identical to its noncognate parent; and ~70% identical to the other hybrid. XPH1 and XPH2 also feature a designed hybrid chameleon sequence corresponding to the C-terminal region, which switched from α-helical to β-sheet structure during Cro evolution. We report solution nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) structures of XPH1 and XPH2 at 0.3 Å and 0.5 Å backbone root mean square deviation (RMSD), respectively. XPH1 retains a global fold generally similar to Xfaso 1, and XPH2 retains a fold similar to Pfl 6, as measured by TM-align scores (~0.7), DALI Z-scores (7-9), and backbone RMSD (2-3 Å RMSD for the most ordered regions). However, these scores also indicate significant deviations in structure. Most notably, XPH1 and XPH2 have different, and intermediate, secondary structure content relative to Xfaso 1 and Pfl 6. The multistep progression in sequence, from Xfaso 1 to XPH1 to XPH2 to Pfl 6, thus involves both abrupt and gradual changes in folding pattern. The plasticity of some protein folds may allow for "polymetamorphic" evolution through intermediate structures.
- Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona, 85721-0088.
Organizational Affiliation: