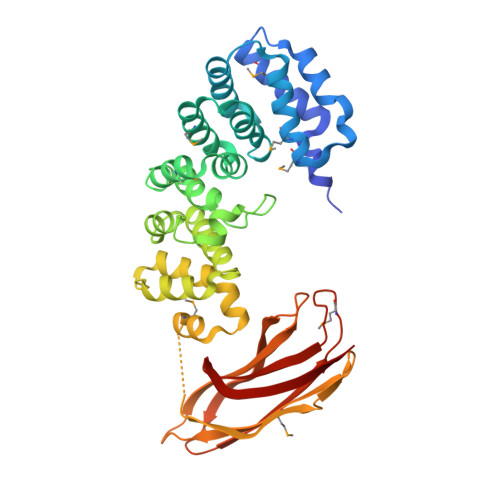
Selective base excision repair of DNA damage by the non-base-flipping DNA glycosylase AlkC.
Shi, R., Mullins, E.A., Shen, X.X., Lay, K.T., Yuen, P.K., David, S.S., Rokas, A., Eichman, B.F.(2018) EMBO J 37: 63-74
- PubMed: 29054852
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201797833
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5VHV, 5VI0 - PubMed Abstract:
DNA glycosylases preserve genome integrity and define the specificity of the base excision repair pathway for discreet, detrimental modifications, and thus, the mechanisms by which glycosylases locate DNA damage are of particular interest. Bacterial AlkC and AlkD are specific for cationic alkylated nucleobases and have a distinctive HEAT-like repeat (HLR) fold. AlkD uses a unique non-base-flipping mechanism that enables excision of bulky lesions more commonly associated with nucleotide excision repair. In contrast, AlkC has a much narrower specificity for small lesions, principally N3-methyladenine (3mA). Here, we describe how AlkC selects for and excises 3mA using a non-base-flipping strategy distinct from that of AlkD. A crystal structure resembling a catalytic intermediate complex shows how AlkC uses unique HLR and immunoglobulin-like domains to induce a sharp kink in the DNA, exposing the damaged nucleobase to active site residues that project into the DNA This active site can accommodate and excise N3-methylcytosine (3mC) and N1-methyladenine (1mA), which are also repaired by AlkB-catalyzed oxidative demethylation, providing a potential alternative mechanism for repair of these lesions in bacteria.
- Department of Biological Sciences, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: