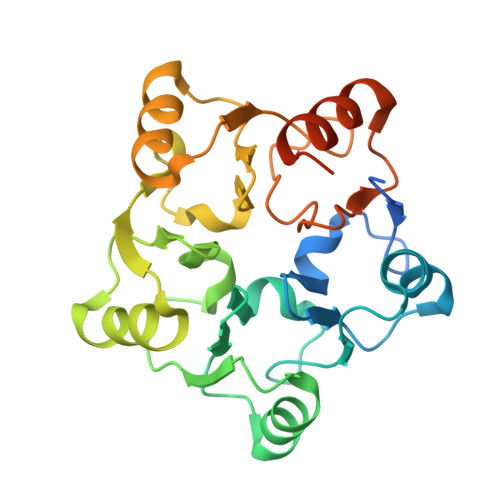
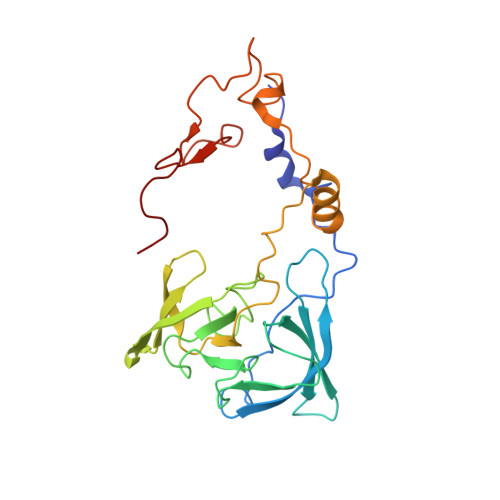
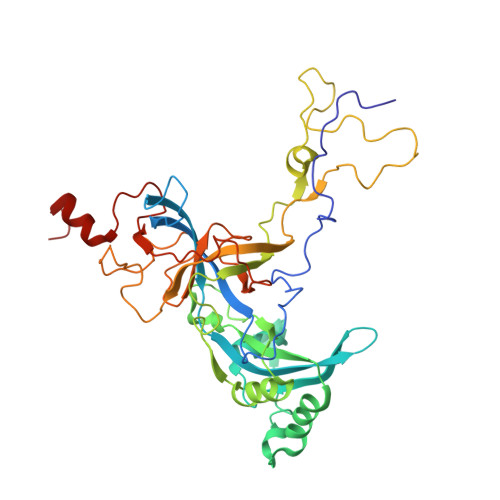
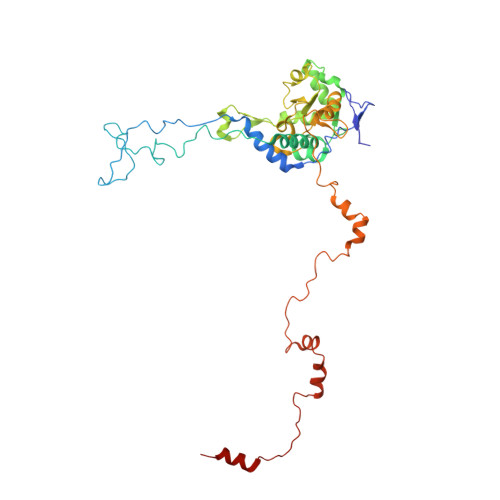
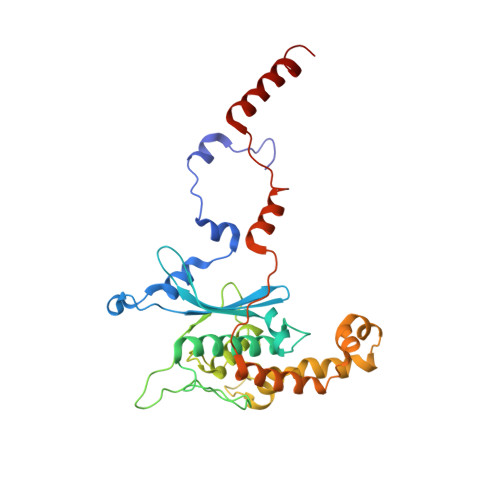
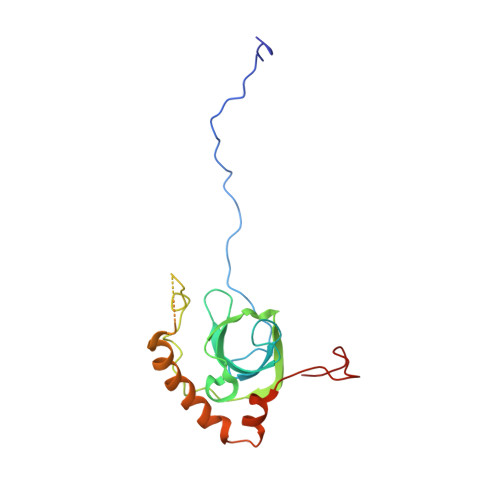
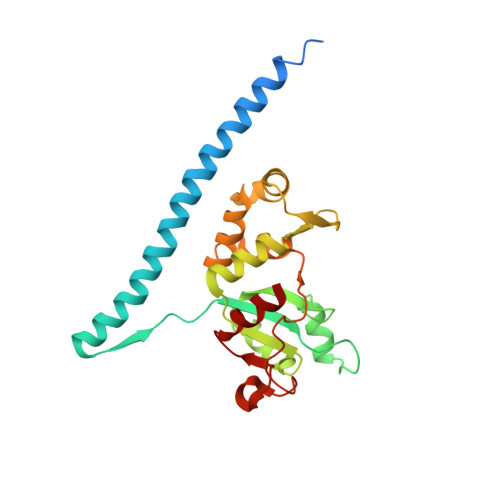
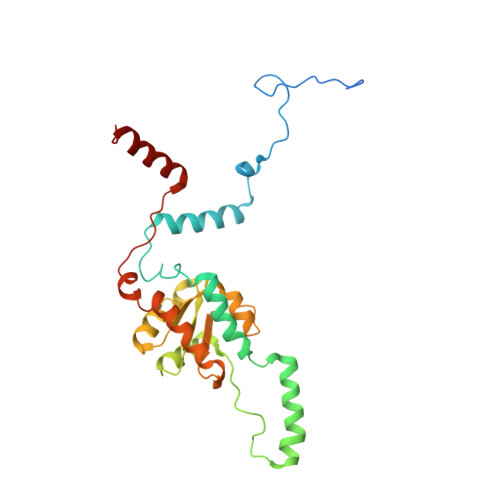
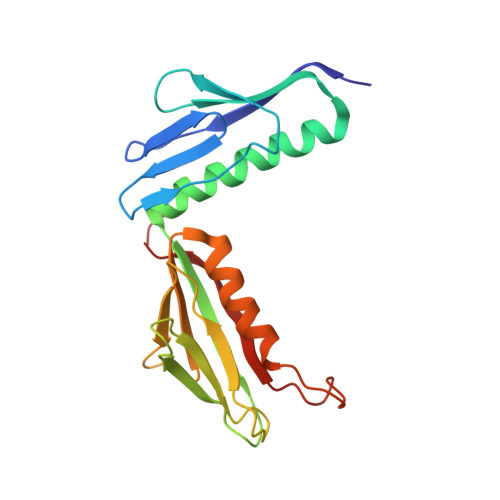
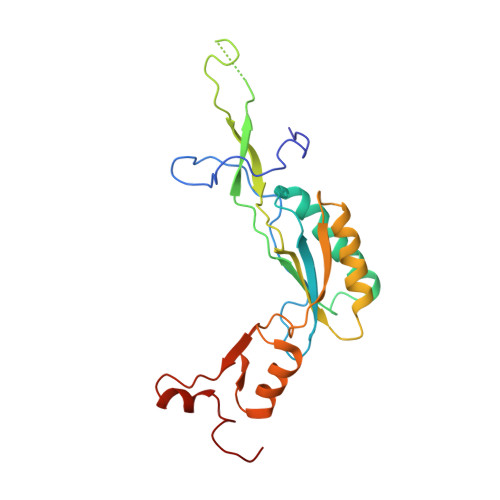
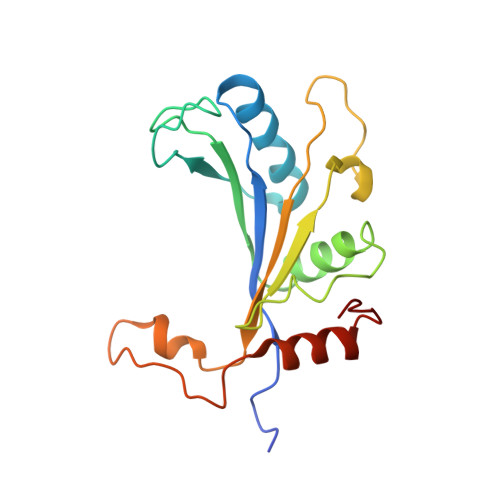
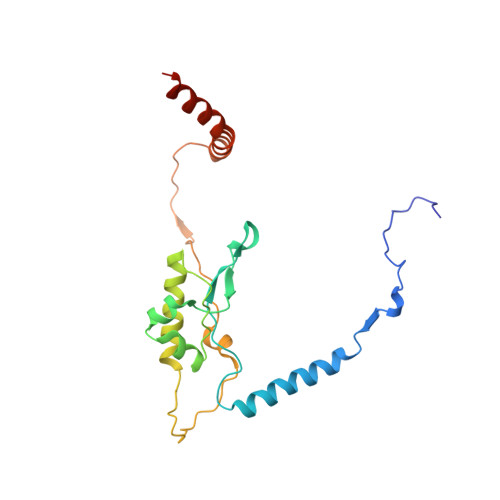
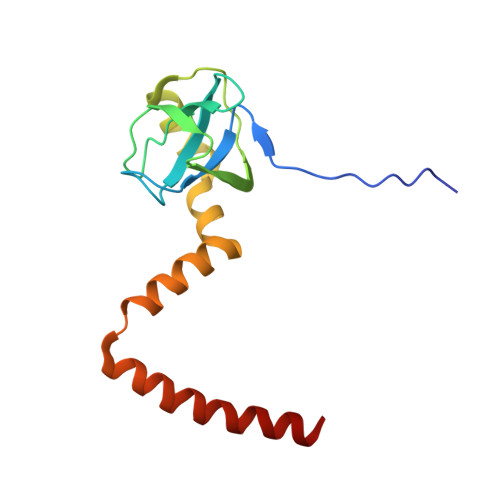
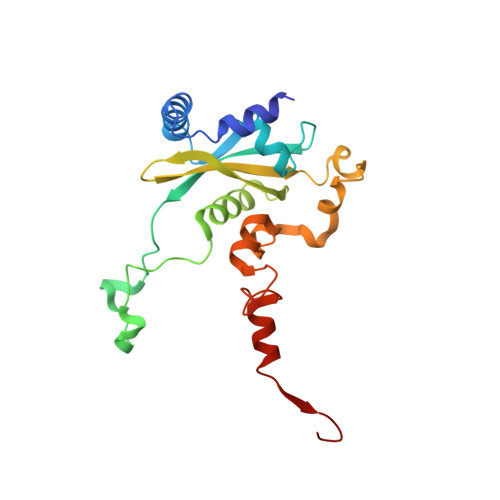
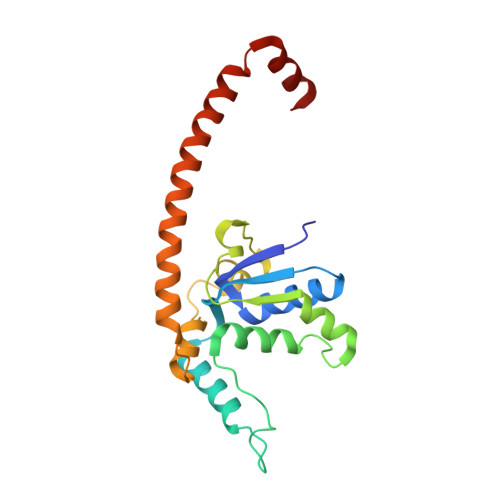
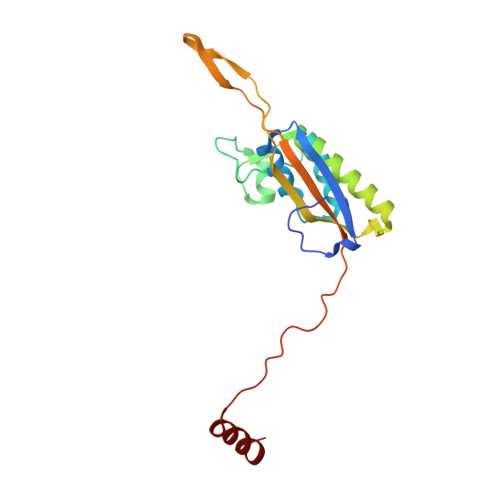
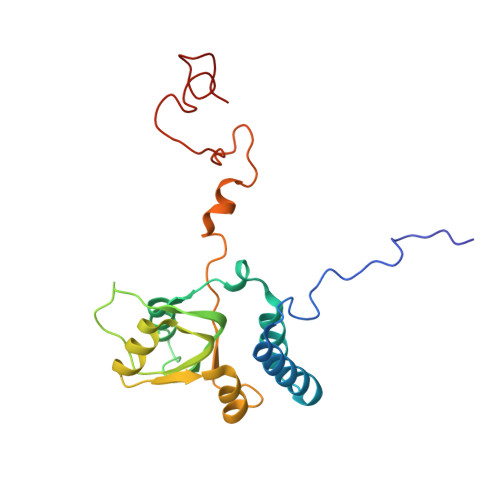
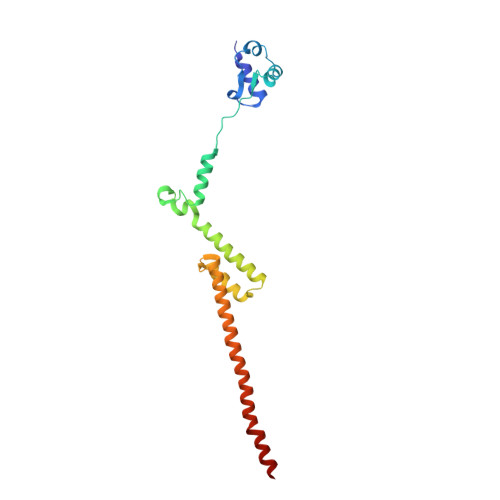
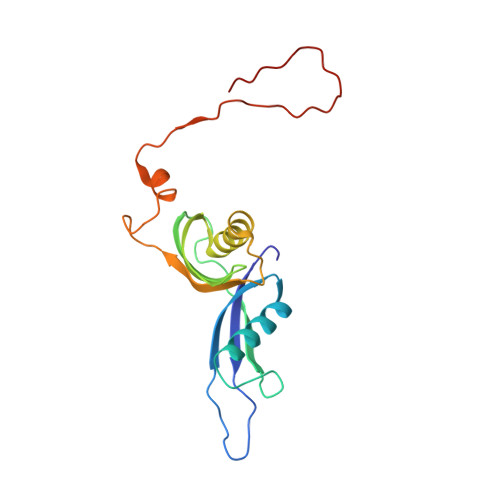
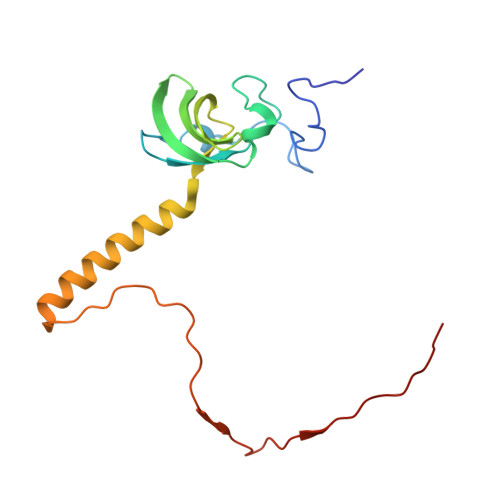
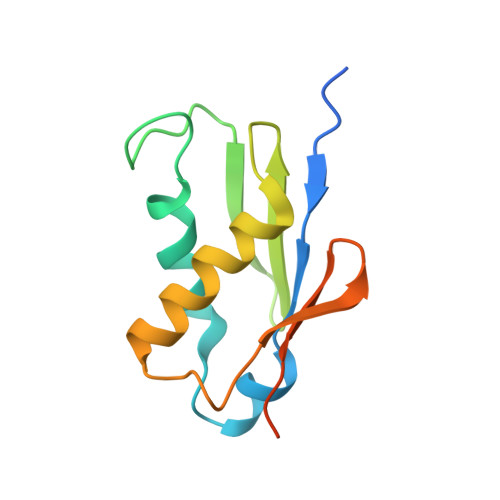
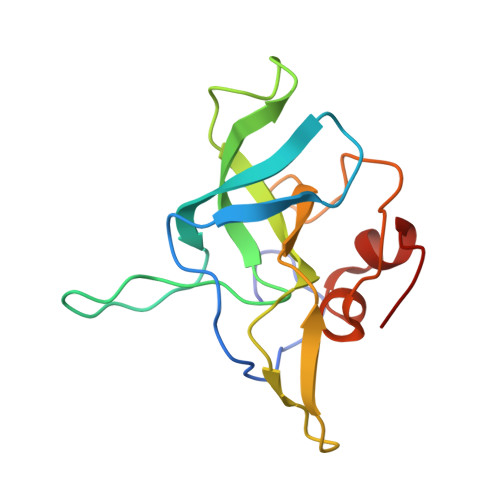
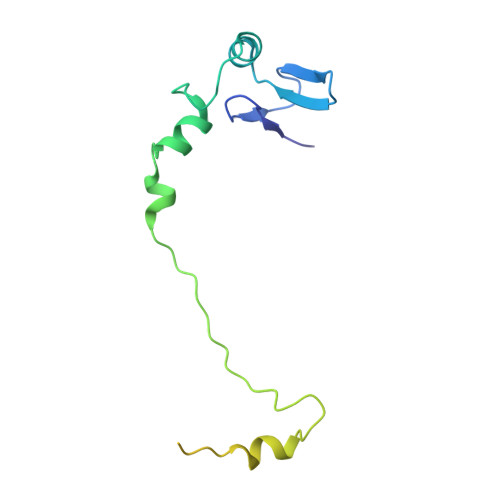
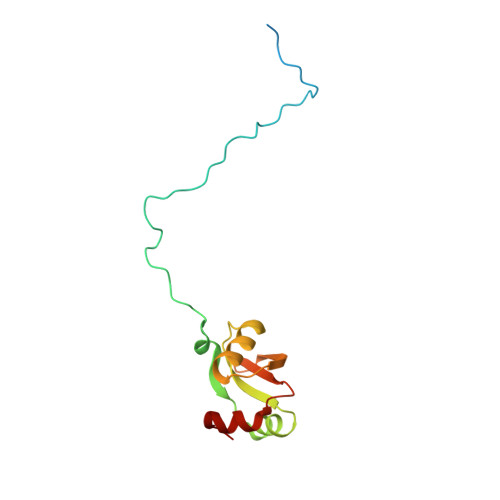
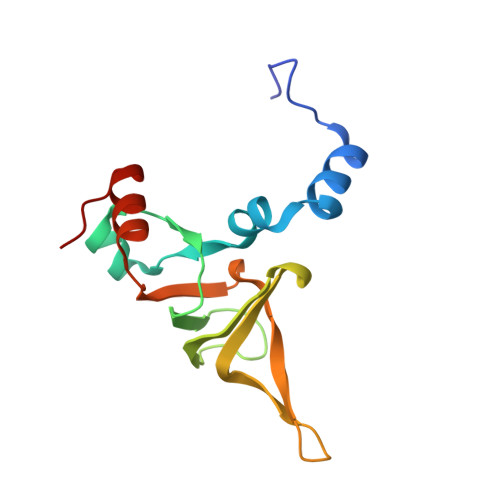
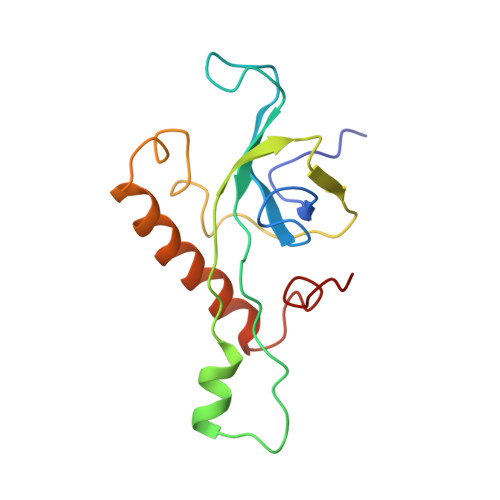
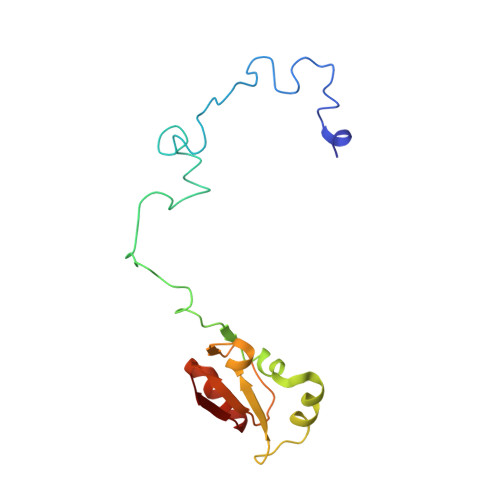
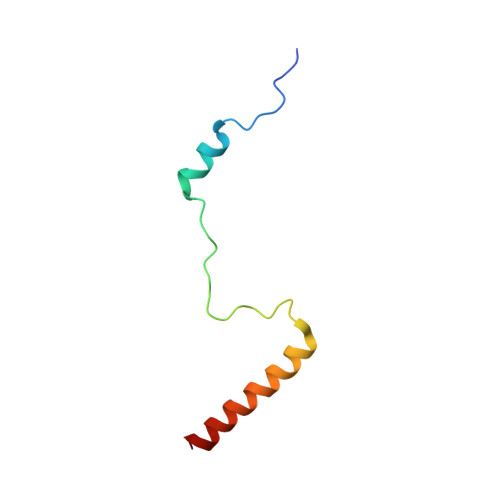
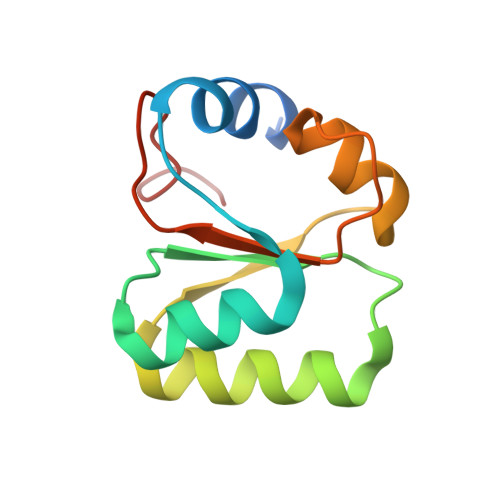
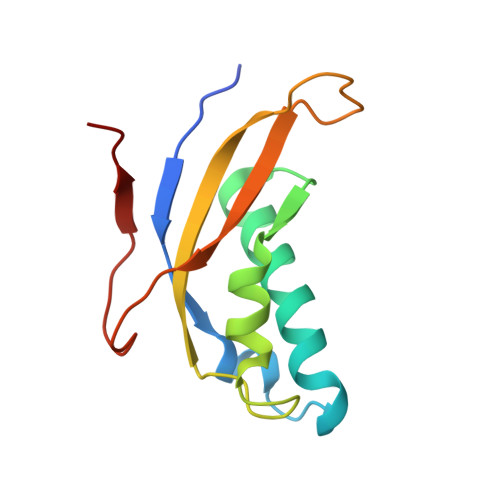
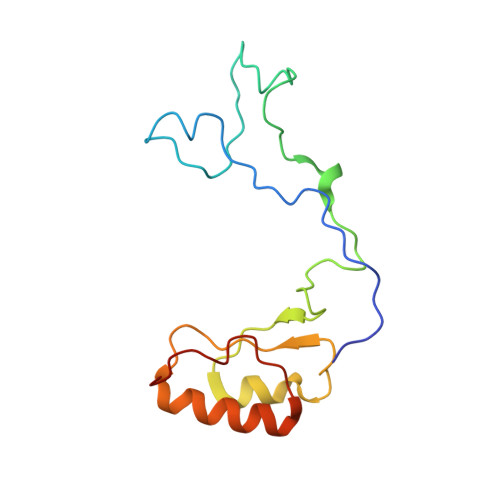
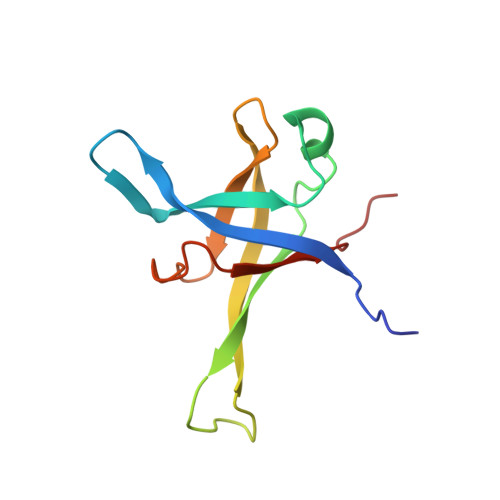
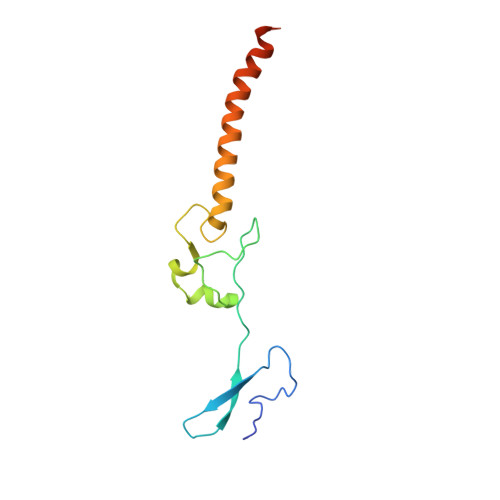
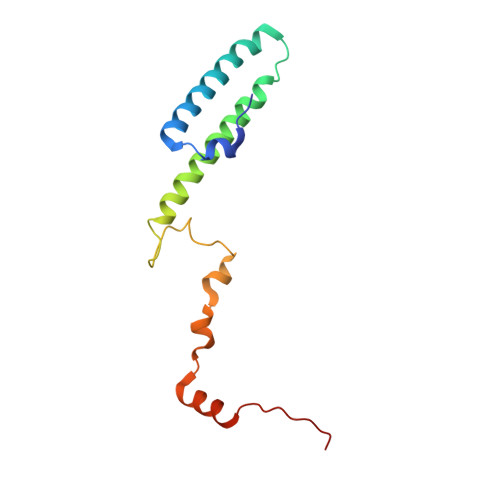
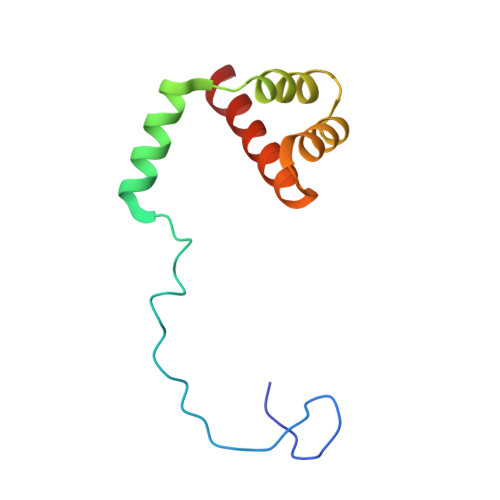
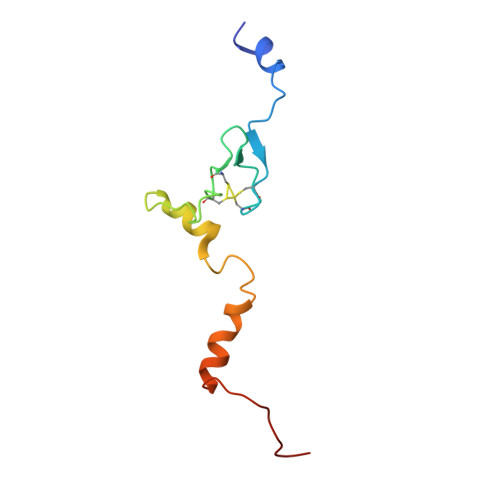
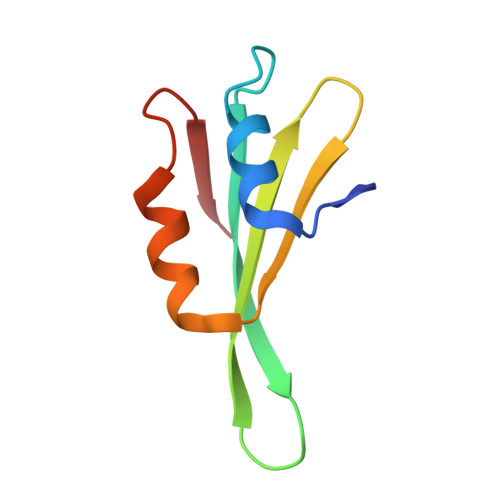
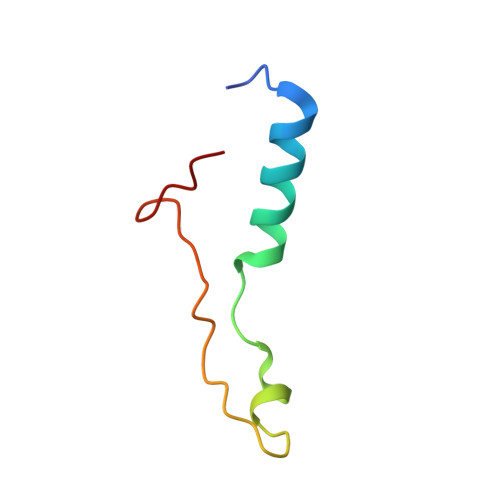
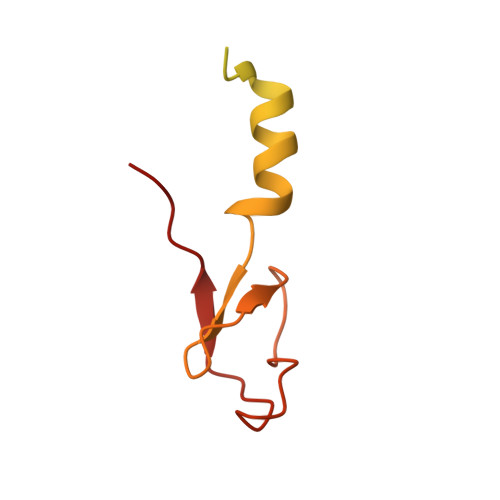
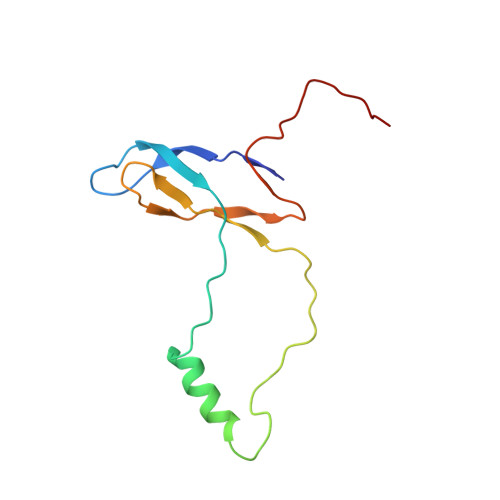
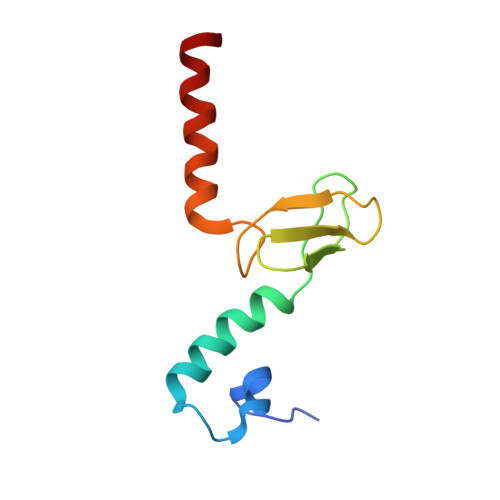
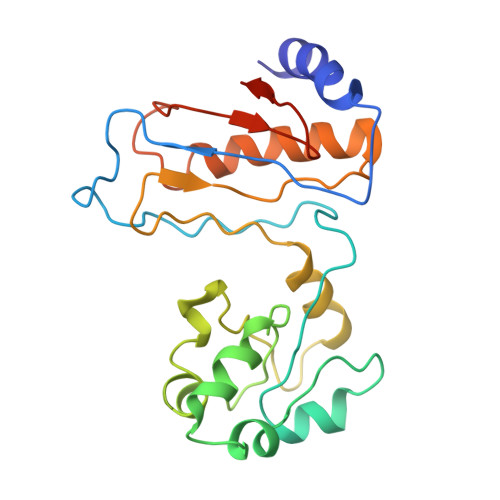
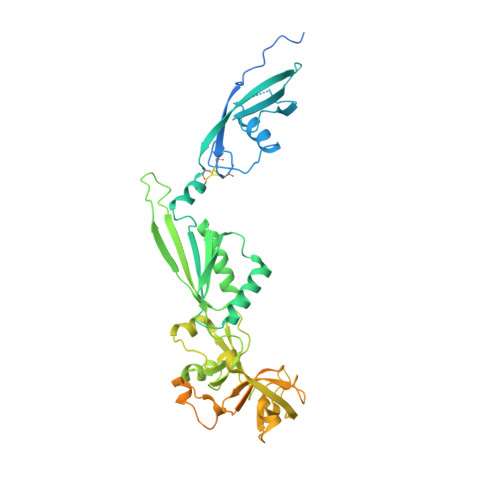
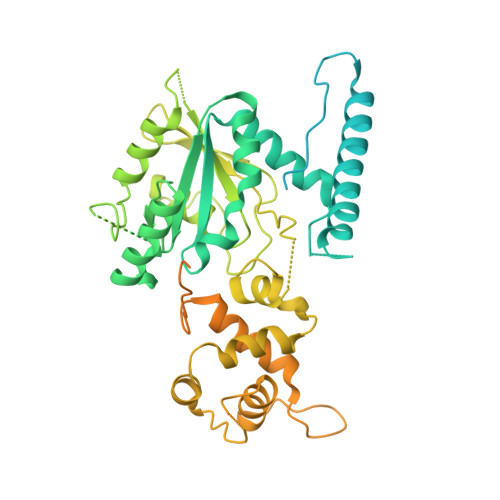
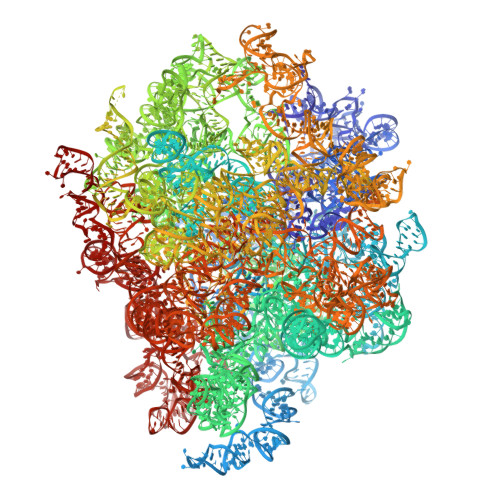
Nmd3 is a structural mimic of eIF5A, and activates the cpGTPase Lsg1 during 60S ribosome biogenesis.
Malyutin, A.G., Musalgaonkar, S., Patchett, S., Frank, J., Johnson, A.W.(2017) EMBO J 36: 854-868
- PubMed: 28179369
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201696012
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5T62, 5T6R - PubMed Abstract:
During ribosome biogenesis in eukaryotes, nascent subunits are exported to the cytoplasm in a functionally inactive state. 60S subunits are activated through a series of cytoplasmic maturation events. The last known events in the cytoplasm are the release of Tif6 by Efl1 and Sdo1 and the release of the export adapter, Nmd3, by the GTPase Lsg1. Here, we have used cryo-electron microscopy to determine the structure of the 60S subunit bound by Nmd3, Lsg1, and Tif6. We find that a central domain of Nmd3 mimics the translation elongation factor eIF5A, inserting into the E site of the ribosome and pulling the L1 stalk into a closed position. Additional domains occupy the P site and extend toward the sarcin-ricin loop to interact with Tif6. Nmd3 and Lsg1 together embrace helix 69 of the B2a intersubunit bridge, inducing base flipping that we suggest may activate the GTPase activity of Lsg1.
- Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics, Columbia University, New York, NY, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: