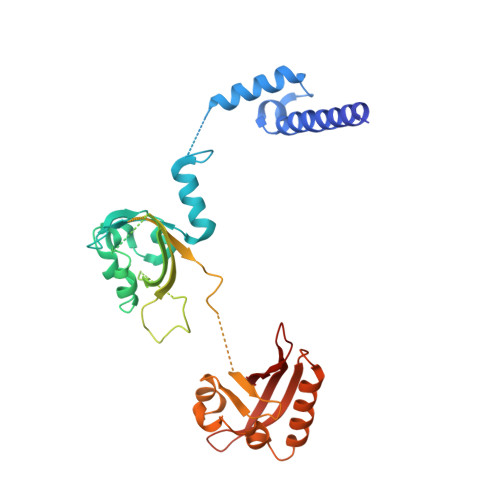
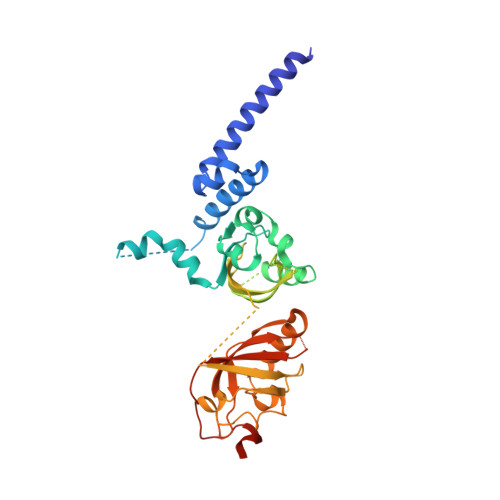
NPAS1-ARNT and NPAS3-ARNT crystal structures implicate the bHLH-PAS family as multi-ligand binding transcription factors.
Wu, D., Su, X., Potluri, N., Kim, Y., Rastinejad, F.(2016) Elife 5
- PubMed: 27782878
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18790
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5SY5, 5SY7 - PubMed Abstract:
The neuronal PAS domain proteins NPAS1 and NPAS3 are members of the basic helix-loop-helix-PER-ARNT-SIM (bHLH-PAS) family, and their genetic deficiencies are linked to a variety of human psychiatric disorders including schizophrenia, autism spectrum disorders and bipolar disease. NPAS1 and NPAS3 must each heterodimerize with the aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (ARNT), to form functional transcription complexes capable of DNA binding and gene regulation. Here we examined the crystal structures of multi-domain NPAS1-ARNT and NPAS3-ARNT-DNA complexes, discovering each to contain four putative ligand-binding pockets. Through expanded architectural comparisons between these complexes and HIF-1α-ARNT, HIF-2α-ARNT and CLOCK-BMAL1, we show the wider mammalian bHLH-PAS family is capable of multi-ligand-binding and presents as an ideal class of transcription factors for direct targeting by small-molecule drugs.
- Integrative Metabolism Program, Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute, Orlando, United States.
Organizational Affiliation: