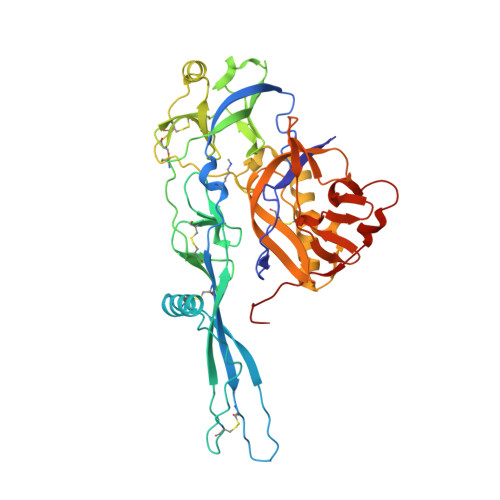
Structural basis for the recognition of LDL-receptor family members by VSV glycoprotein.
Nikolic, J., Belot, L., Raux, H., Legrand, P., Gaudin, Y., A Albertini, A.(2018) Nat Commun 9: 1029-1029
- PubMed: 29531262
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03432-4
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5OY9, 5OYL - PubMed Abstract:
Vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) is an oncolytic rhabdovirus and its glycoprotein G is widely used to pseudotype other viruses for gene therapy. Low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDL-R) serves as a major entry receptor for VSV. Here we report two crystal structures of VSV G in complex with two distinct cysteine-rich domains (CR2 and CR3) of LDL-R, showing that their binding sites on G are identical. We identify two basic residues on G, which are essential for its interaction with CR2 and CR3. Mutating these residues abolishes VSV infectivity even though VSV can use alternative receptors, indicating that all VSV receptors are members of the LDL-R family. Collectively, our data suggest that VSV G has specifically evolved to interact with receptor CR domains. These structural insights into the interaction between VSV G and host cell receptors provide a basis for the design of recombinant viruses with an altered tropism.
- Institute for Integrative Biology of the Cell (I2BC), CEA, CNRS, Univ. Paris-Sud, Université Paris-Saclay, 91198, Gif-sur-Yvette cedex, France.
Organizational Affiliation: