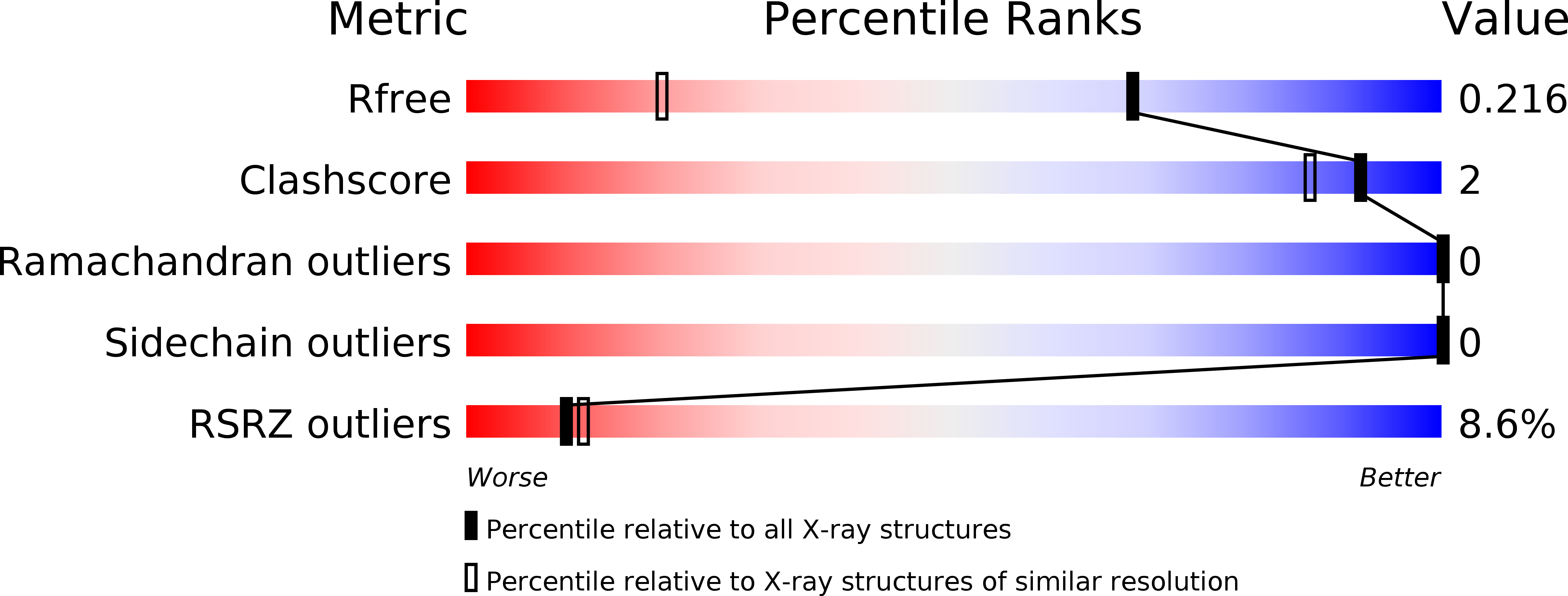
The Crystal Structure of Gurmarin, a Sweet Taste-Suppressing Protein: Identification of the Amino Acid Residues Essential for Inhibition.
Sigoillot, M., Brockhoff, A., Neiers, F., Poirier, N., Belloir, C., Legrand, P., Charron, C., Roblin, P., Meyerhof, W., Briand, L.(2018) Chem Senses 43: 635-643
- PubMed: 30137256
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/chemse/bjy054
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5OLL - PubMed Abstract:
Gurmarin is a highly specific sweet taste-suppressing protein in rodents that is isolated from the Indian plant Gymnema sylvestre. Gurmarin consists of 35 amino acid residues containing 3 intramolecular disulfide bridges that form a cystine knot. Here, we report the crystal structure of gurmarin at a 1.45 Å resolution and compare it with previously reported nuclear magnetic resonance solution structures. The atomic structure at this resolution allowed us to identify a very flexible region consisting of hydrophobic residues. Some of these amino acid residues had been identified as a putative binding site for the rat sweet taste receptor in a previous study. By combining alanine-scanning mutagenesis of the gurmarin molecule and a functional cell-based receptor assay, we confirmed that some single point mutations in these positions drastically affect sweet taste receptor inhibition by gurmarin.
Organizational Affiliation:
INRA, CNRS, Centre des Sciences du Goût et de l'Alimentation, Université de Bourgogne-Franche Comté, Dijon, France.