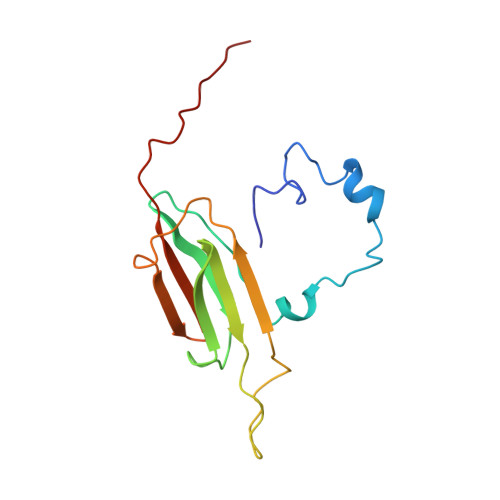
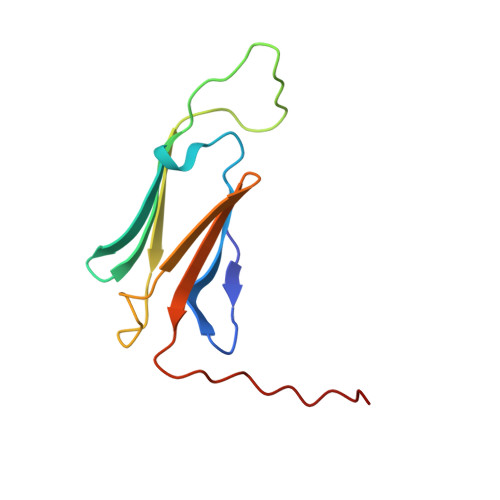
Structural model of dodecameric heat-shock protein Hsp21: Flexible N-terminal arms interact with client proteins while C-terminal tails maintain the dodecamer and chaperone activity.
Rutsdottir, G., Harmark, J., Weide, Y., Hebert, H., Rasmussen, M.I., Wernersson, S., Respondek, M., Akke, M., Hjrup, P., Koeck, P.J.B., Soderberg, C.A.G., Emanuelsson, C.(2017) J Biological Chem 292: 8103-8121
- PubMed: 28325834
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M116.766816
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5NMS - PubMed Abstract:
Small heat-shock proteins (sHsps) prevent aggregation of thermosensitive client proteins in a first line of defense against cellular stress. The mechanisms by which they perform this function have been hard to define due to limited structural information; currently, there is only one high-resolution structure of a plant sHsp published, that of the cytosolic Hsp16.9. We took interest in Hsp21, a chloroplast-localized sHsp crucial for plant stress resistance, which has even longer N-terminal arms than Hsp16.9, with a functionally important and conserved methionine-rich motif. To provide a framework for investigating structure-function relationships of Hsp21 and understanding these sequence variations, we developed a structural model of Hsp21 based on homology modeling, cryo-EM, cross-linking mass spectrometry, NMR, and small-angle X-ray scattering. Our data suggest a dodecameric arrangement of two trimer-of-dimer discs stabilized by the C-terminal tails, possibly through tail-to-tail interactions between the discs, mediated through extended I X V X I motifs. Our model further suggests that six N-terminal arms are located on the outside of the dodecamer, accessible for interaction with client proteins, and distinct from previous undefined or inwardly facing arms. To test the importance of the I X V X I motif, we created the point mutant V181A, which, as expected, disrupts the Hsp21 dodecamer and decreases chaperone activity. Finally, our data emphasize that sHsp chaperone efficiency depends on oligomerization and that client interactions can occur both with and without oligomer dissociation. These results provide a generalizable workflow to explore sHsps, expand our understanding of sHsp structural motifs, and provide a testable Hsp21 structure model to inform future investigations.
- From the Departments of Biochemistry and Structural Biology and.
Organizational Affiliation: