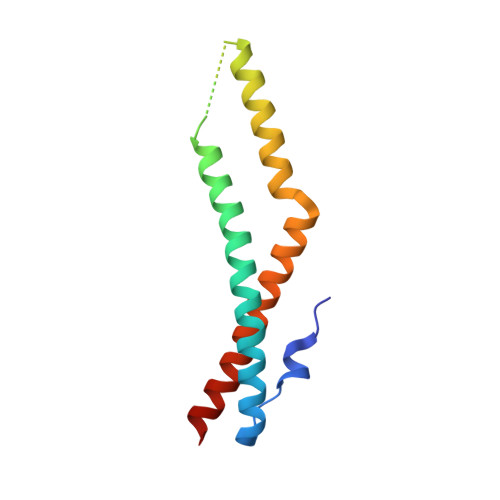
Crystal structure of the tricellulin C-terminal coiled-coil domain reveals a unique mode of dimerization.
Schuetz, A., Radusheva, V., Krug, S.M., Heinemann, U.(2017) Ann N Y Acad Sci 1405: 147-159
- PubMed: 28661558
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.13408
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5N7H, 5N7I, 5N7K - PubMed Abstract:
Tricellulin is a tight junction protein localized to tricellular contacts in many epithelial tissues, where it is required for full barrier control. Here, we present crystal structures of the tricellulin C-terminal coiled-coil domain, revealing a potential dimeric arrangement. By combining structural, biochemical, functional, and mutation analyses, we gain insight into the mode of tricellulin oligomerization and suggest a model where dimerization of its cytoplasmic C-terminus may play an auxiliary role in stabilizing homophilic and potentially also heterophilic cis-interactions within tight junctions.
- Helmholtz Protein Sample Production Facility, Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine, Berlin, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: