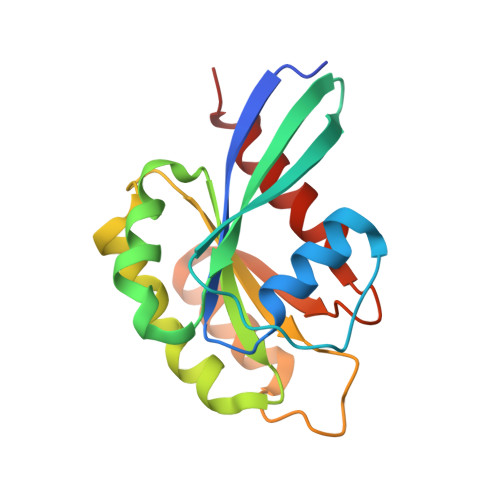
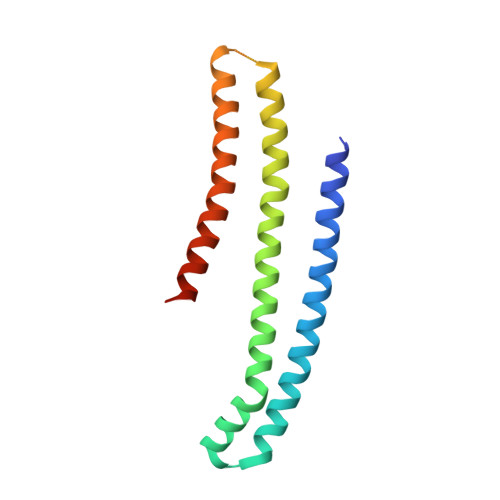
bMERB domains are bivalent Rab8 family effectors evolved by gene duplication.
Rai, A., Oprisko, A., Campos, J., Fu, Y., Friese, T., Itzen, A., Goody, R.S., Gazdag, E.M., Muller, M.P.(2016) Elife 5
- PubMed: 27552051
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18675
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5LPN, 5SZG, 5SZH, 5SZI, 5SZJ, 5SZK - PubMed Abstract:
In their active GTP-bound form, Rab proteins interact with proteins termed effector molecules. In this study, we have thoroughly characterized a Rab effector domain that is present in proteins of the Mical and EHBP families, both known to act in endosomal trafficking. Within our study, we show that these effectors display a preference for Rab8 family proteins (Rab8, 10, 13 and 15) and that some of the effector domains can bind two Rab proteins via separate binding sites. Structural analysis allowed us to explain the specificity towards Rab8 family members and the presence of two similar Rab binding sites that must have evolved via gene duplication. This study is the first to thoroughly characterize a Rab effector protein that contains two separate Rab binding sites within a single domain, allowing Micals and EHBPs to bind two Rabs simultaneously, thus suggesting previously unknown functions of these effector molecules in endosomal trafficking.
- Department of Structural Biochemistry, Max Planck Institute of Molecular Physiology, Dortmund, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: