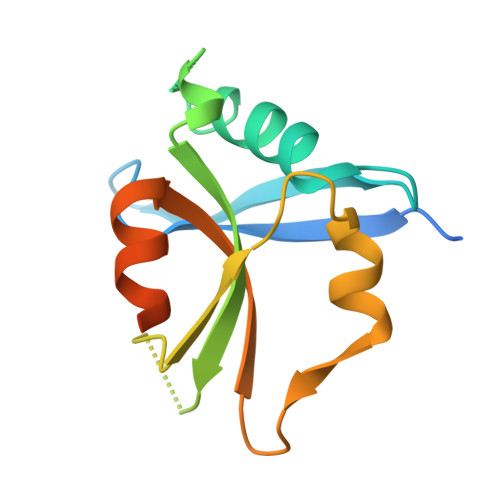
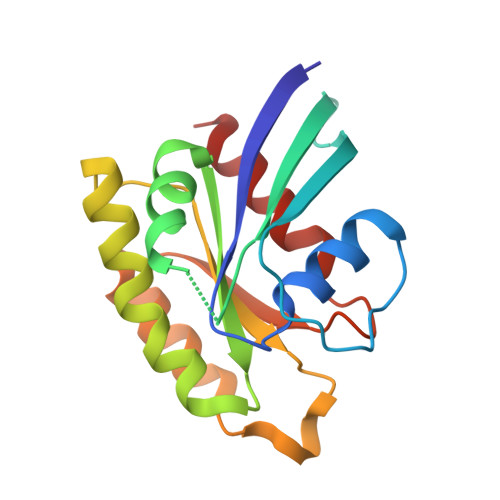
Structural Basis of Dimeric Rasip1 RA Domain Recognition of the Ras Subfamily of GTP-Binding Proteins.
Gingras, A.R., Puzon-McLaughlin, W., Bobkov, A.A., Ginsberg, M.H.(2016) Structure 24: 2152-2162
- PubMed: 27839947
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2016.10.001
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5KHO, 5KHQ - PubMed Abstract:
Ras-interacting protein 1 (Rasip1) is an endothelial-specific Rap1 and Ras effector, important for vascular development and angiogenesis. Here, we report the crystal structure of the Rasip1 RA domain (RRA) alone, revealing the basis of dimerization, and in complex with Rap1 at 2.8 Å resolution. In contrast to most RA domains, RRA formed a dimer that can bind two Rap1 (K D = 0.9 μM) or Ras (K D = 2.2 μM) molecules. We solved the Rap1-RRA complex and found that Rasip1 binds Rap1 in the Switch I region, and Rap1 binding induces few conformation changes to Rasip1 stabilizing a β strand and an unstructured loop. Our data explain how Rasip1 can act as a Rap1 and Ras effector and show that Rasip1 defines a subgroup of dimeric RA domains that could mediate cooperative binding to membrane-associated Ras superfamily members.
- Department of Medicine, University of California San Diego, 9500 Gilman Drive, La Jolla, CA 92093, USA. Electronic address: agingras@ucsd.edu.
Organizational Affiliation: