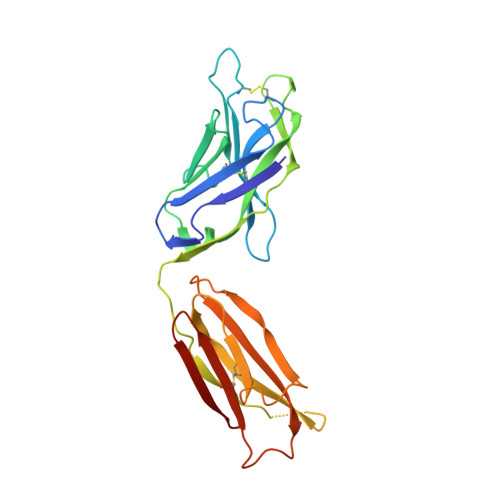
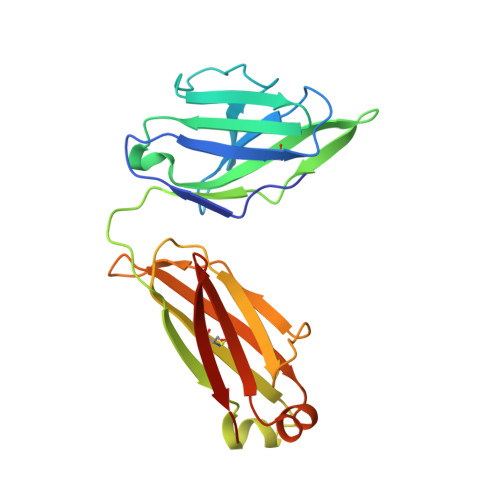
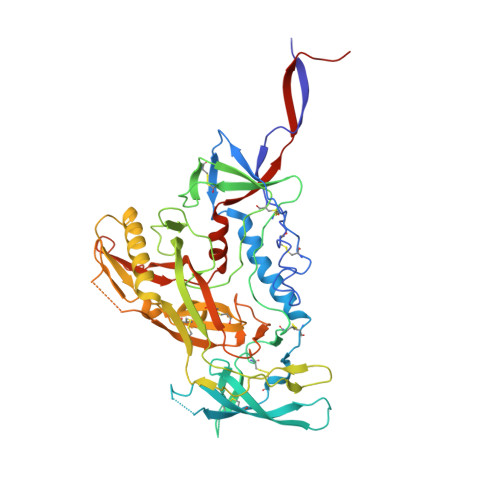
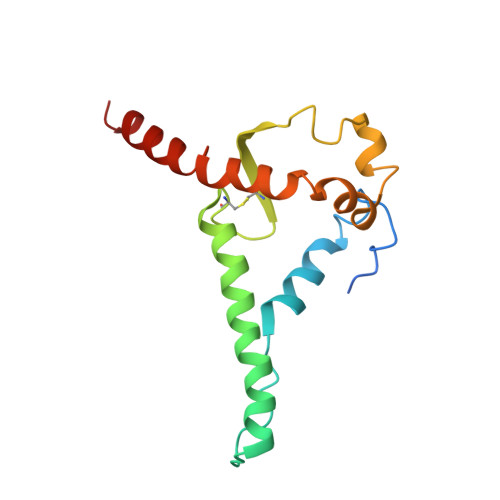
Uncleaved prefusion-optimized gp140 trimers derived from analysis of HIV-1 envelope metastability.
Kong, L., He, L., de Val, N., Vora, N., Morris, C.D., Azadnia, P., Sok, D., Zhou, B., Burton, D.R., Ward, A.B., Wilson, I.A., Zhu, J.(2016) Nat Commun 7: 12040-12040
- PubMed: 27349805
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12040
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5JS9, 5JSA - PubMed Abstract:
The trimeric HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein (Env) is critical for host immune recognition and neutralization. Despite advances in trimer design, the roots of Env trimer metastability remain elusive. Here we investigate the contribution of two Env regions to metastability. First, we computationally redesign a largely disordered bend in heptad region 1 (HR1) of SOSIP trimers that connects the long, central HR1 helix to the fusion peptide, substantially improving the yield of soluble, well-folded trimers. Structural and antigenic analyses of two distinct HR1 redesigns confirm that redesigned Env closely mimics the native, prefusion trimer with a more stable gp41. Next, we replace the cleavage site between gp120 and gp41 with various linkers in the context of an HR1 redesign. Electron microscopy reveals a potential fusion intermediate state for uncleaved trimers containing short but not long linkers. Together, these results outline a general approach for stabilization of Env trimers from diverse HIV-1 strains.
- Department of Integrative Structural and Computational Biology, The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, California 92037, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: