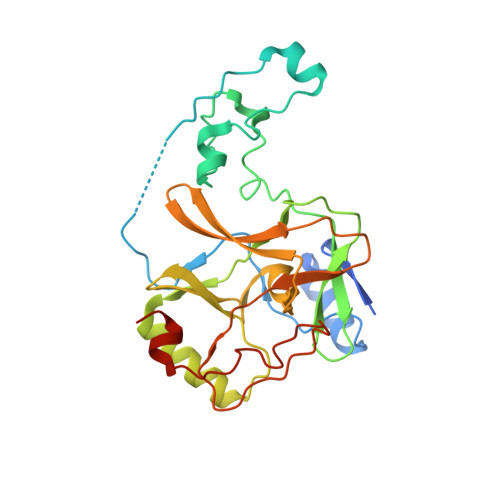
Molecular basis for oncohistone H3 recognition by SETD2 methyltransferase
Yang, S., Zheng, X., Lu, C., Li, G.M., Allis, C.D., Li, H.(2016) Genes Dev 30: 1611-1616
- PubMed: 27474439
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.284323.116
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5JJY, 5JLB, 5JLE - PubMed Abstract:
High-frequency point mutations of genes encoding histones have been identified recently as novel drivers in a number of tumors. Specifically, the H3K36M/I mutations were shown to be oncogenic in chondroblastomas and undifferentiated sarcomas by inhibiting H3K36 methyltransferases, including SETD2. Here we report the crystal structures of the SETD2 catalytic domain bound to H3K36M or H3K36I peptides with SAH (S-adenosylhomocysteine). In the complex structure, the catalytic domain adopts an open conformation, with the K36M/I peptide snuggly positioned in a newly formed substrate channel. Our structural and biochemical data reveal the molecular basis underying oncohistone recognition by and inhibition of SETD2.
- MOE Key Laboratory of Protein Sciences, Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Structural Biology, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China; Department of Basic Medical Sciences, School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China;
Organizational Affiliation: