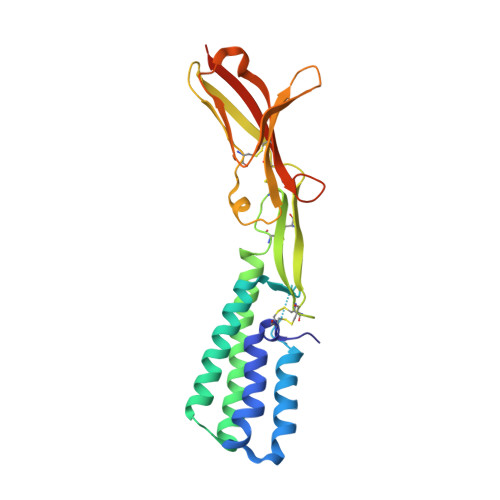
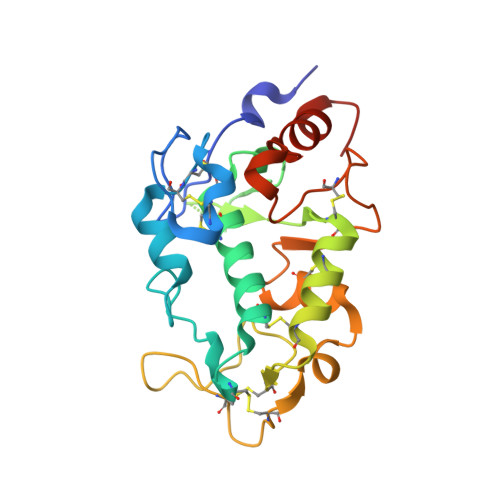
Structure of IZUMO1-JUNO reveals sperm-oocyte recognition during mammalian fertilization
Ohto, U., Ishida, H., Krayukhina, E., Uchiyama, S., Inoue, N., Shimizu, T.(2016) Nature 534: 566-569
- PubMed: 27309808
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature18596
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5JK9, 5JKA, 5JKB, 5JKC, 5JKD, 5JKE - PubMed Abstract:
Fertilization is a fundamental process in sexual reproduction, creating a new individual through the combination of male and female gametes. The IZUMO1 sperm membrane protein and its counterpart oocyte receptor JUNO have been identified as essential factors for sperm-oocyte interaction and fusion. However, the mechanism underlying their specific recognition remains poorly defined. Here, we show the crystal structures of human IZUMO1, JUNO and the IZUMO1-JUNO complex, establishing the structural basis for the IZUMO1-JUNO-mediated sperm-oocyte interaction. IZUMO1 exhibits an elongated rod-shaped structure comprised of a helical bundle IZUMO domain and an immunoglobulin-like domain that are each firmly anchored to an intervening β-hairpin region through conserved disulfide bonds. The central β-hairpin region of IZUMO1 provides the main platform for JUNO binding, while the surface located behind the putative JUNO ligand binding pocket is involved in IZUMO1 binding. Structure-based mutagenesis analysis confirms the biological importance of the IZUMO1-JUNO interaction. This structure provides a major step towards elucidating an essential phase of fertilization and it will contribute to the development of new therapeutic interventions for fertility, such as contraceptive agents.
- Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, The University of Tokyo, Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: