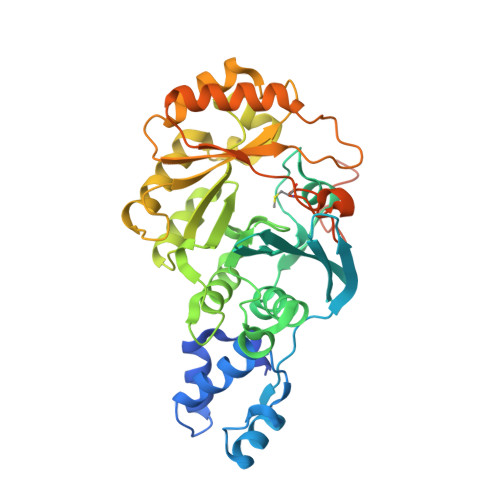
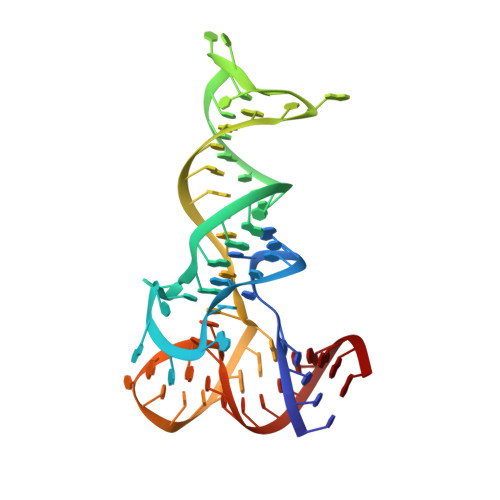
Crystallographic capture of a radical S-adenosylmethionine enzyme in the act of modifying tRNA.
Schwalm, E.L., Grove, T.L., Booker, S.J., Boal, A.K.(2016) Science 352: 309-312
- PubMed: 27081063
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aad5367
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5HR6, 5HR7 - PubMed Abstract:
RlmN is a dual-specificity RNA methylase that modifies C2 of adenosine 2503 (A2503) in 23S rRNA and C2 of adenosine 37 (A37) in several Escherichia coli transfer RNAs (tRNAs). A related methylase, Cfr, modifies C8 of A2503 via a similar mechanism, conferring resistance to multiple classes of antibiotics. Here, we report the x-ray structure of a key intermediate in the RlmN reaction, in which a Cys(118)→Ala variant of the protein is cross-linked to a tRNA(Glu)substrate through the terminal methylene carbon of a formerly methylcysteinyl residue and C2 of A37. RlmN contacts the entire length of tRNA(Glu), accessing A37 by using an induced-fit strategy that completely unfolds the tRNA anticodon stem-loop, which is likely critical for recognition of both tRNA and ribosomal RNA substrates.
- Department of Chemistry, Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 16802, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: