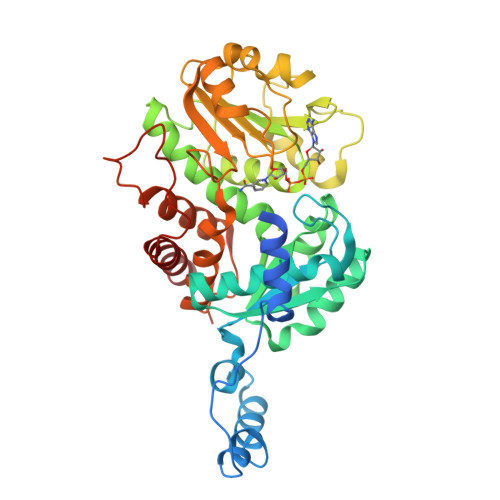
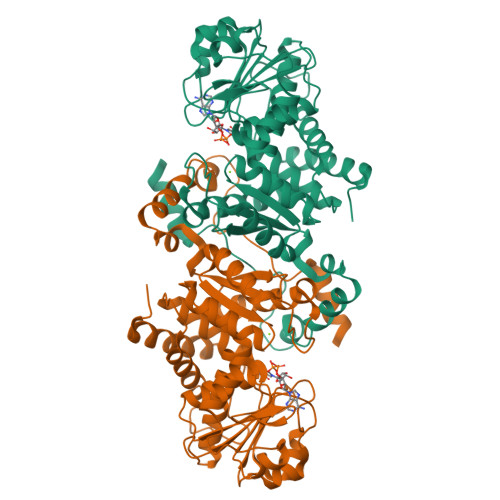
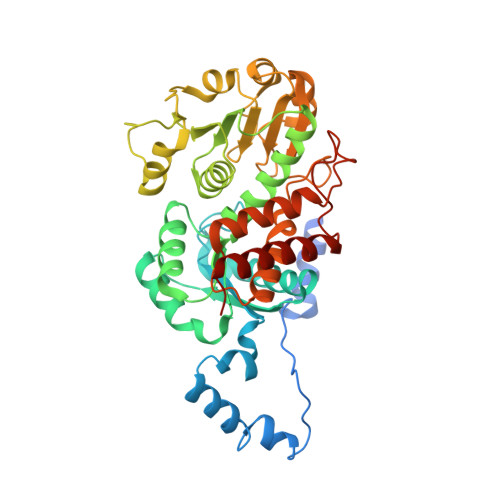
The crystal structure of the malic enzyme from Candidatus Phytoplasma reveals the minimal structural determinants for a malic enzyme.
Alvarez, C.E., Trajtenberg, F., Larrieux, N., Saigo, M., Golic, A., Andreo, C.S., Hogenhout, S.A., Mussi, M.A., Drincovich, M.F., Buschiazzo, A.(2018) Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol 74: 332-340
- PubMed: 29652260
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2059798318002759
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5CEE - PubMed Abstract:
Phytoplasmas are wall-less phytopathogenic bacteria that produce devastating effects in a wide variety of plants. Reductive evolution has shaped their genome, with the loss of many genes, limiting their metabolic capacities. Owing to the high concentration of C 4 compounds in plants, and the presence of malic enzyme (ME) in all phytoplasma genomes so far sequenced, the oxidative decarboxylation of L-malate might represent an adaptation to generate energy. Aster yellows witches'-broom (Candidatus Phytoplasma) ME (AYWB-ME) is one of the smallest of all characterized MEs, yet retains full enzymatic activity. Here, the crystal structure of AYWB-ME is reported, revealing a unique fold that differs from those of `canonical' MEs. AYWB-ME is organized as a dimeric species formed by intertwining of the N-terminal domains of the protomers. As a consequence of such structural differences, key catalytic residues such as Tyr36 are positioned in the active site of each protomer but are provided by the other protomer of the dimer. A Tyr36Ala mutation abolishes the catalytic activity, indicating the key importance of this residue in the catalytic process but not in the dimeric assembly. Phylogenetic analyses suggest that larger MEs (large-subunit or chimeric MEs) might have evolved from this type of smaller scaffold by gaining small sequence cassettes or an entire functional domain. The Candidatus Phytoplasma AYWB-ME structure showcases a novel minimal structure design comprising a fully functional active site, making this enzyme an attractive starting point for rational genetic design.
Organizational Affiliation:
CEFOBI, Suipacha 531, Rosario, S2000LRJ Santa Fe, Argentina.