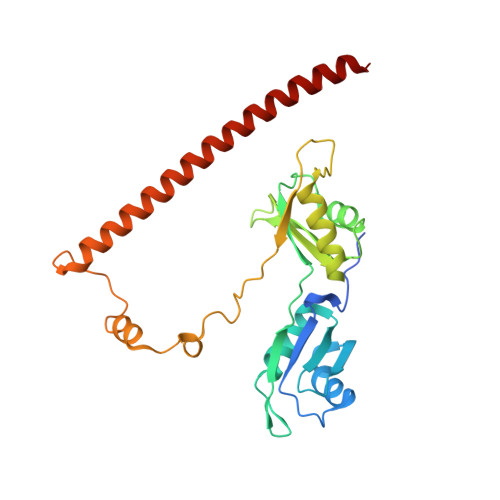
Caenorhabditis elegans NONO-1: Insights into DBHS protein structure, architecture, and function.
Knott, G.J., Lee, M., Passon, D.M., Fox, A.H., Bond, C.S.(2015) Protein Sci 24: 2033-2043
- PubMed: 26435036
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.2816
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5CA5 - PubMed Abstract:
Members of the Drosophila behavior/human splicing (DBHS) protein family have been characterized in the vertebrates Homo sapiens and Mus musculus, and the invertebrates Drosophila melanogaster and Chironomus tentans. Collectively, both vertebrate and invertebrate DBHS proteins function throughout gene regulation, largely but not always, within the nucleus. In this study, we report a structural and bioinformatic analysis of the DBHS protein family to guide future studies into DBHS protein function. To explore the structural plasticity of the family, we describe the 2.4 Å crystal structure of Caenorhabditis elegans non-POU domain-containing octamer-binding protein 1 (NONO-1). The structure is dimeric, with a domain arrangement consistent with mammalian DBHS proteins. Comparison with the DBHS structures available from H. sapiens reveals that there is inherent domain flexibility within the homologous DBHS region. Mapping amino acid similarity within the family to the NONO-1 dimer highlights the dimer interface, coiled-coil oligomerization motif, and putative RNA binding surfaces. Surprisingly, the interior surface of RNA recognition motif 2 (RRM2) that faces a large internal void is highly variable, but the external β2-β3 loops of RRM2 show remarkable preservation. Overall, the DBHS region is under strong purifying selection, whereas the sequences N- and C-terminal to the DBHS region are less constrained. The findings described in this study provide a molecular basis for further investigation into the mechanistic function of the DBHS protein family in biology.
- School of Chemistry and Biochemistry, The University of Western Australia, Crawley, Western Australia, 6009, Australia.
Organizational Affiliation: