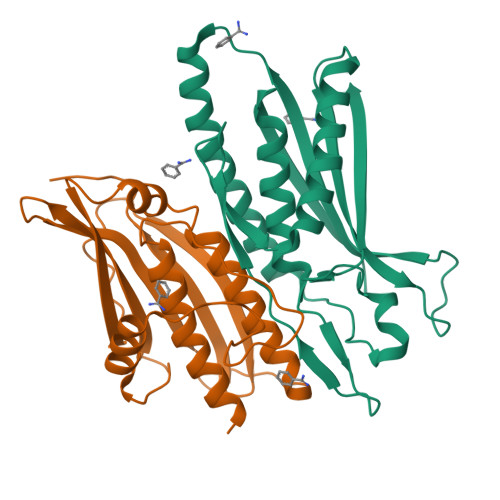
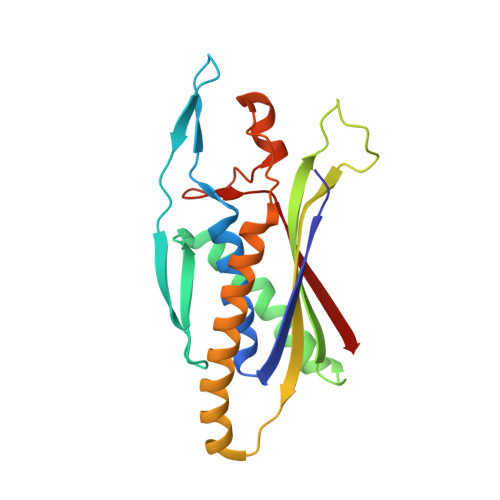
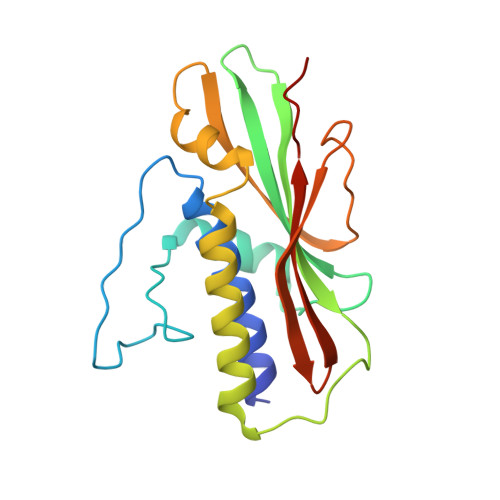
Structure of the Human Atg13-Atg101 HORMA Heterodimer: an Interaction Hub within the ULK1 Complex.
Qi, S., Kim, D.J., Stjepanovic, G., Hurley, J.H.(2015) Structure 23: 1848-1857
- PubMed: 26299944
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2015.07.011
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5C50 - PubMed Abstract:
The ULK1 complex, consisting of the ULK1 protein kinase itself, FIP200, Atg13, and Atg101, controls the initiation of autophagy in animals. We determined the structure of the complex of the human Atg13 HORMA (Hop1, Rev7, Mad2) domain in complex with the full-length HORMA domain-only protein Atg101. The two HORMA domains assemble with an architecture conserved in the Mad2 conformational heterodimer and the S. pombe Atg13-Atg101 HORMA complex. The WF finger motif that is essential for function in human Atg101 is sequestered in a hydrophobic pocket, suggesting that the exposure of this motif is regulated. Benzamidine molecules from the crystallization solution mark two hydrophobic pockets that are conserved in, and unique to, animals, and are suggestive of sites that could interact with other proteins. These features suggest that the activity of the animal Atg13-Atg101 subcomplex is regulated and that it is an interaction hub for multiple partners.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular and Cell Biology, California Institute for Quantitative Biosciences, University of California, Berkeley, Berkeley, CA 94720, USA.