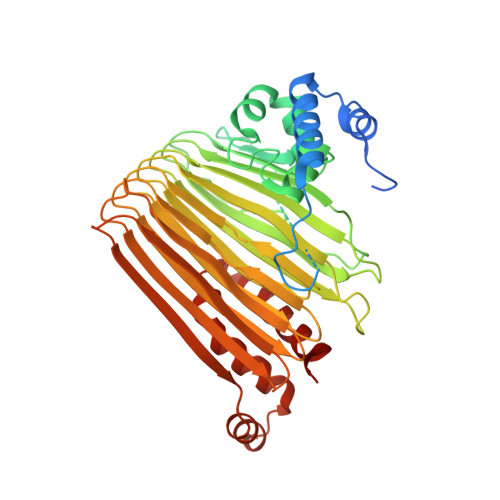
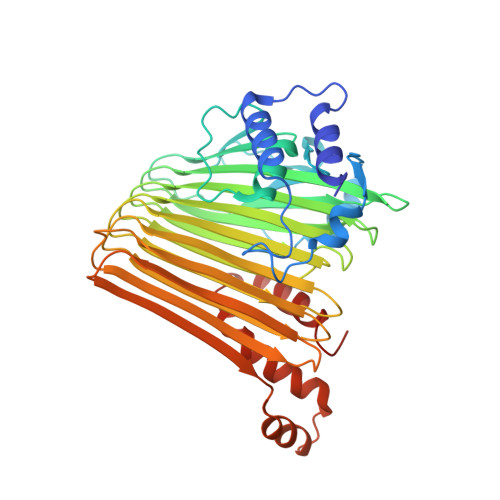
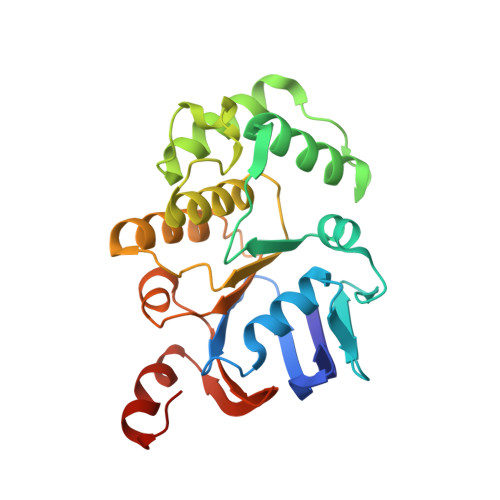
Functional Dynamics Revealed by the Structure of the SufBCD Complex, a Novel ATP-binding Cassette (ABC) Protein That Serves as a Scaffold for Iron-Sulfur Cluster Biogenesis
Hirabayashi, K., Yuda, E., Tanaka, N., Katayama, S., Iwasaki, K., Matsumoto, T., Kurisu, G., Outten, F.W., Fukuyama, K., Takahashi, Y., Wada, K.(2015) J Biological Chem 290: 29717-29731
- PubMed: 26472926
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.680934
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5AWF, 5AWG - PubMed Abstract:
ATP-binding cassette (ABC)-type ATPases are chemomechanical engines involved in diverse biological pathways. Recent genomic information reveals that ABC ATPase domains/subunits act not only in ABC transporters and structural maintenance of chromosome proteins, but also in iron-sulfur (Fe-S) cluster biogenesis. A novel type of ABC protein, the SufBCD complex, functions in the biosynthesis of nascent Fe-S clusters in almost all Eubacteria and Archaea, as well as eukaryotic chloroplasts. In this study, we determined the first crystal structure of the Escherichia coli SufBCD complex, which exhibits the common architecture of ABC proteins: two ABC ATPase components (SufC) with function-specific components (SufB-SufD protomers). Biochemical and physiological analyses based on this structure provided critical insights into Fe-S cluster assembly and revealed a dynamic conformational change driven by ABC ATPase activity. We propose a molecular mechanism for the biogenesis of the Fe-S cluster in the SufBCD complex.
- From the Department of Biological Sciences, Graduate School of Science, Osaka University, Osaka 560-0043, Japan, the Organization for Promotion of Tenure Track, University of Miyazaki, Miyazaki 889-1692, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: