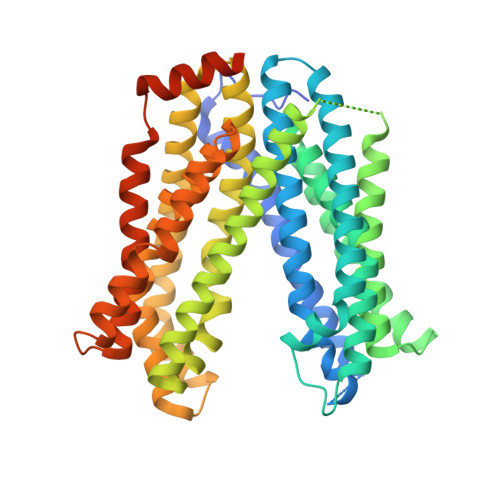
MATE transport of the E. coli-derived genotoxin colibactin.
Mousa, J.J., Yang, Y., Tomkovich, S., Shima, A., Newsome, R.C., Tripathi, P., Oswald, E., Bruner, S.D., Jobin, C.(2016) Nat Microbiol 1: 15009-15009
- PubMed: 27571755
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmicrobiol.2015.9
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4Z3N, 4Z3P - PubMed Abstract:
Various forms of cancer have been linked to the carcinogenic activities of microorganisms(1-3). The virulent gene island polyketide synthase (pks) produces the secondary metabolite colibactin, a genotoxic molecule(s) causing double-stranded DNA breaks(4) and enhanced colorectal cancer development(5,6). Colibactin biosynthesis involves a prodrug resistance strategy where an N-terminal prodrug scaffold (precolibactin) is assembled, transported into the periplasm and cleaved to release the mature product(7-10). Here, we show that ClbM, a multidrug and toxic compound extrusion (MATE) transporter, is a key component involved in colibactin activity and transport. Disruption of clbM attenuated pks+ E. coli-induced DNA damage in vitro and significantly decreased the DNA damage response in gnotobiotic Il10(-/-) mice. Colonization experiments performed in mice or zebrafish animal models indicate that clbM is not implicated in E. coli niche establishment. The X-ray structure of ClbM shows a structural motif common to the recently described MATE family. The 12-transmembrane ClbM is characterized as a cation-coupled antiporter, and residues important to the cation-binding site are identified. Our data identify ClbM as a precolibactin transporter and provide the first structure of a MATE transporter with a defined and specific biological function.
- Department of Chemistry, University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida 32611, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: