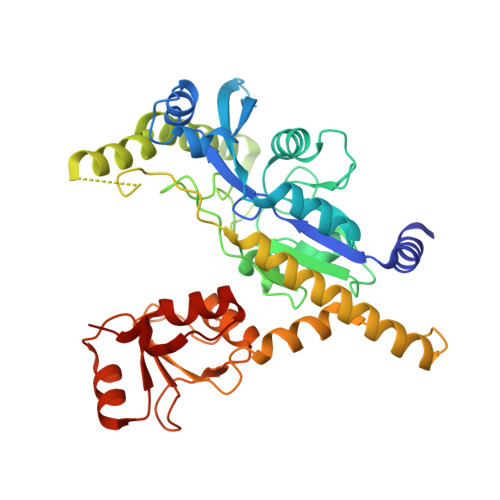
Genetic and structural analysis of the essential fission yeast RNA polymerase II CTD phosphatase Fcp1.
Schwer, B., Ghosh, A., Sanchez, A.M., Lima, C.D., Shuman, S.(2015) RNA 21: 1135-1146
- PubMed: 25883047
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.050286.115
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4XPZ, 4XQ0 - PubMed Abstract:
Protein phosphatases regulate mRNA synthesis and processing by remodeling the carboxy-terminal domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase II (Pol2) to dynamically inscribe a Pol2 CTD code. Fission yeast Fcp1 (SpFcp1) is an essential 723-amino acid CTD phosphatase that preferentially hydrolyzes Ser2-PO4 of the YS(2)PTSPS repeat. The SpFcp1 catalytic domain (aa 140-580) is composed of a DxDxT acyl-phosphatase module (FCPH) and a BRCT module. Here we conducted a genetic analysis of SpFcp1, which shows that (i) phosphatase catalytic activity is required for vegetative growth of fission yeast; (ii) the flanking amino-terminal domain (aa 1-139) and its putative metal-binding motif C(99)H(101)Cys(109)C(112) are essential; (iii) the carboxy-terminal domain (aa 581-723) is dispensable; (iv) a structurally disordered internal segment of the FCPH domain (aa 330-393) is dispensable; (v) lethal SpFcp1 mutations R271A and R299A are rescued by shortening the Pol2 CTD repeat array; and (vi) CTD Ser2-PO4 is not the only essential target of SpFcp1 in vivo. Recent studies highlight a second CTD code involving threonine phosphorylation of a repeat motif in transcription elongation factor Spt5. We find that Fcp1 can dephosphorylate Thr1-PO4 of the fission yeast Spt5 CTD nonamer repeat T(1)PAWNSGSK. We identify Arg271 as a governor of Pol2 versus Spt5 CTD substrate preference. Our findings implicate Fcp1 as a versatile sculptor of both the Pol2 and Spt5 CTD codes. Finally, we report a new 1.45 Å crystal structure of SpFcp1 with Mg(2+) and AlF3 that mimics an associative phosphorane transition state of the enzyme-aspartyl-phosphate hydrolysis reaction.
- Microbiology and Immunology Department, Weill Cornell Medical College, New York, New York 10065, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: