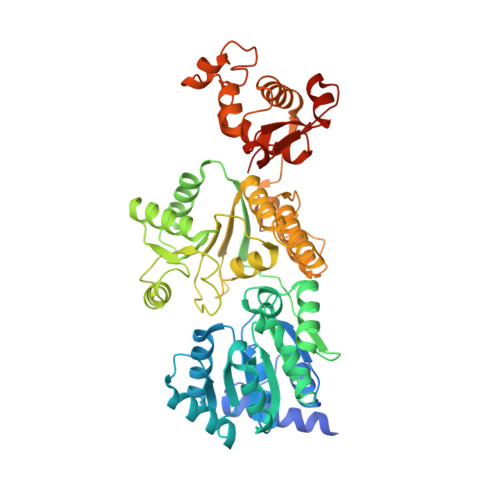
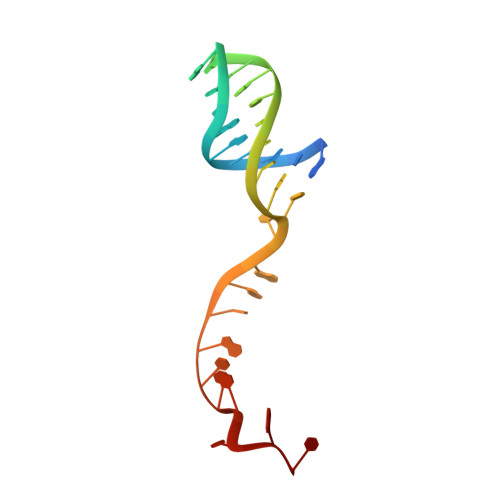Structural mechanisms of DNA binding and unwinding in bacterial RecQ helicases.
Manthei, K.A., Hill, M.C., Burke, J.E., Butcher, S.E., Keck, J.L.(2015) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112: 4292-4297
- PubMed: 25831501
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1416746112
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4TMU - PubMed Abstract:
RecQ helicases unwind remarkably diverse DNA structures as key components of many cellular processes. How RecQ enzymes accommodate different substrates in a unified mechanism that couples ATP hydrolysis to DNA unwinding is unknown. Here, the X-ray crystal structure of the Cronobacter sakazakii RecQ catalytic core domain bound to duplex DNA with a 3' single-stranded extension identifies two DNA-dependent conformational rearrangements: a winged-helix domain pivots ∼90° to close onto duplex DNA, and a conserved aromatic-rich loop is remodeled to bind ssDNA. These changes coincide with a restructuring of the RecQ ATPase active site that positions catalytic residues for ATP hydrolysis. Complex formation also induces a tight bend in the DNA and melts a portion of the duplex. This bending, coupled with translocation, could provide RecQ with a mechanism for unwinding duplex and other DNA structures.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biomolecular Chemistry, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, WI 53706; and.