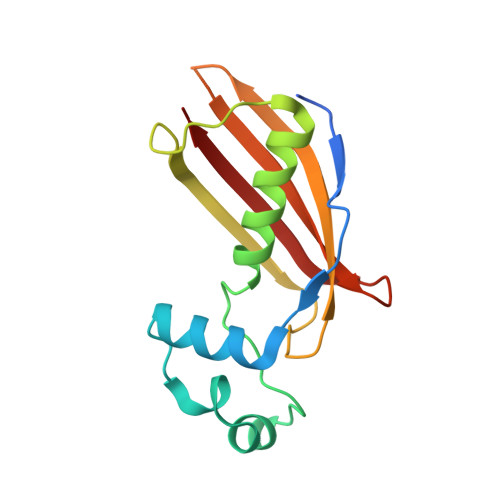
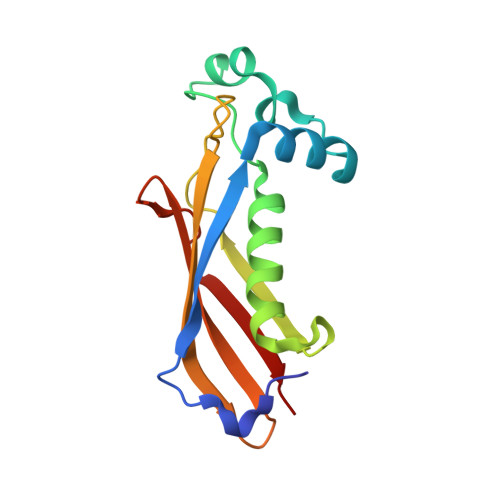
Crystal structure of dehydratase component HadAB complex of mycobacterial FAS-II pathway.
Biswas, R., Dutta, A., Dutta, D., Hazra, D., Banerjee, D.R., Basak, A., Das, A.K.(2015) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 458: 369-374
- PubMed: 25656575
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.01.119
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4RV2 - PubMed Abstract:
Fatty acid biosynthesis type II in mycobacteria delivers the fatty acids required for mycolic acid synthesis. The pathway employs a unique maoC like β-hydroxyacyl-ACP dehydratase HadAB or HadBC heterodimer in the third step of the elongation cycle. Here we report the crystal structure of the HadAB complex determined using a Pb-SIRAS method. Crystal structure aided with enzymatic study establishes the roles of HadA as a scaffolding component and HadB as a catalytic component together indispensable for the activity. The detailed structural analysis of HadAB in combination with MD simulation endorses the spatial orientation of the central hot-dog helix and the dynamic nature of its associated loop in regulation of substrate specificities in dehydratase/hydratase family enzymes.
- Department of Biotechnology, Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur, Kharagpur 721302, India.
Organizational Affiliation: