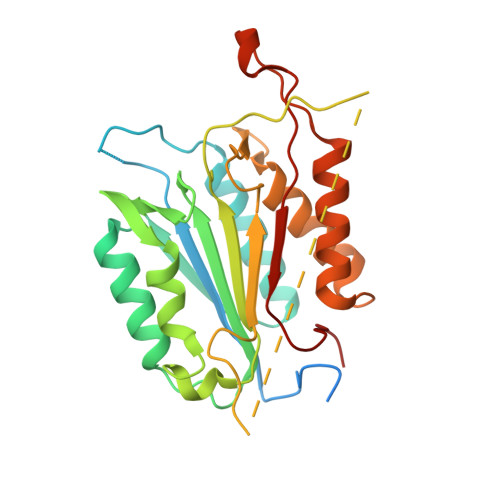
Modifying caspase-3 activity by altering allosteric networks.
Cade, C., Swartz, P., MacKenzie, S.H., Clark, A.C.(2014) Biochemistry 53: 7582-7595
- PubMed: 25343534
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi500874k
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4QTX, 4QTY, 4QU0, 4QU5, 4QU8, 4QU9, 4QUA, 4QUB, 4QUD, 4QUE, 4QUG, 4QUH, 4QUI, 4QUJ, 4QUL - PubMed Abstract:
Caspases have several allosteric sites that bind small molecules or peptides. Allosteric regulators are known to affect caspase enzyme activity, in general, by facilitating large conformational changes that convert the active enzyme to a zymogen-like form in which the substrate-binding pocket is disordered. Mutations in presumed allosteric networks also decrease activity, although large structural changes are not observed. Mutation of the central V266 to histidine in the dimer interface of caspase-3 inactivates the enzyme by introducing steric clashes that may ultimately affect positioning of a helix on the protein surface. The helix is thought to connect several residues in the active site to the allosteric dimer interface. In contrast to the effects of small molecule allosteric regulators, the substrate-binding pocket is intact in the mutant, yet the enzyme is inactive. We have examined the putative allosteric network, in particular the role of helix 3, by mutating several residues in the network. We relieved steric clashes in the context of caspase-3(V266H), and we show that activity is restored, particularly when the restorative mutation is close to H266. We also mimicked the V266H mutant by introducing steric clashes elsewhere in the allosteric network, generating several mutants with reduced activity. Overall, the data show that the caspase-3 native ensemble includes the canonical active state as well as an inactive conformation characterized by an intact substrate-binding pocket, but with an altered helix 3. The enzyme activity reflects the relative population of each species in the native ensemble.
- Department of Molecular and Structural Biochemistry and ‡Center for Comparative Medicine and Translational Research, North Carolina State University , Raleigh, North Carolina 27695, United States.
Organizational Affiliation: