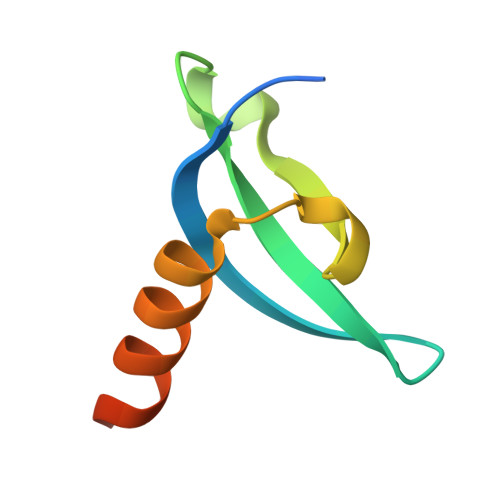
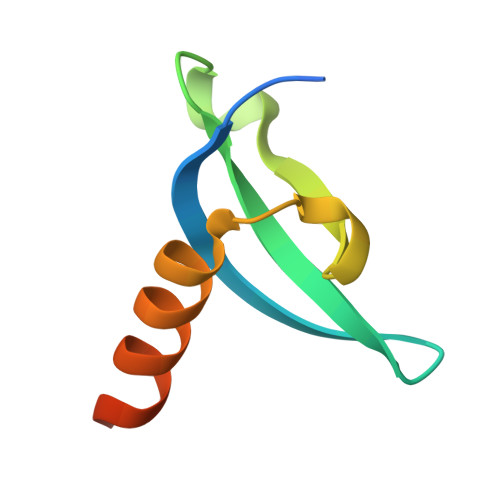
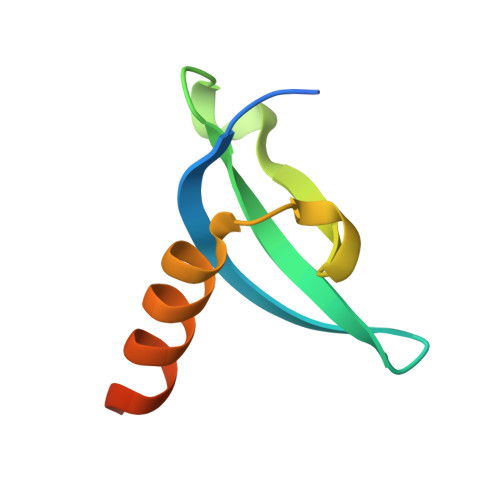
Transgenerationally inherited piRNAs trigger piRNA biogenesis by changing the chromatin of piRNA clusters and inducing precursor processing.
Le Thomas, A., Stuwe, E., Li, S., Du, J., Marinov, G., Rozhkov, N., Chen, Y.C., Luo, Y., Sachidanandam, R., Toth, K.F., Patel, D., Aravin, A.A.(2014) Genes Dev 28: 1667-1680
- PubMed: 25085419
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.245514.114
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4QUC, 4QUF - PubMed Abstract:
Small noncoding RNAs that associate with Piwi proteins, called piRNAs, serve as guides for repression of diverse transposable elements in germ cells of metazoa. In Drosophila, the genomic regions that give rise to piRNAs, the so-called piRNA clusters, are transcribed to generate long precursor molecules that are processed into mature piRNAs. How genomic regions that give rise to piRNA precursor transcripts are differentiated from the rest of the genome and how these transcripts are specifically channeled into the piRNA biogenesis pathway are not known. We found that transgenerationally inherited piRNAs provide the critical trigger for piRNA production from homologous genomic regions in the next generation by two different mechanisms. First, inherited piRNAs enhance processing of homologous transcripts into mature piRNAs by initiating the ping-pong cycle in the cytoplasm. Second, inherited piRNAs induce installment of the histone 3 Lys9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) mark on genomic piRNA cluster sequences. The heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1) homolog Rhino binds to the H3K9me3 mark through its chromodomain and is enriched over piRNA clusters. Rhino recruits the piRNA biogenesis factor Cutoff to piRNA clusters and is required for efficient transcription of piRNA precursors. We propose that transgenerationally inherited piRNAs act as an epigenetic memory for identification of substrates for piRNA biogenesis on two levels: by inducing a permissive chromatin environment for piRNA precursor synthesis and by enhancing processing of these precursors.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Biology, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, California 91125, USA; Ecole Doctorale Complexité du Vivant, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, 75005 Paris, France;