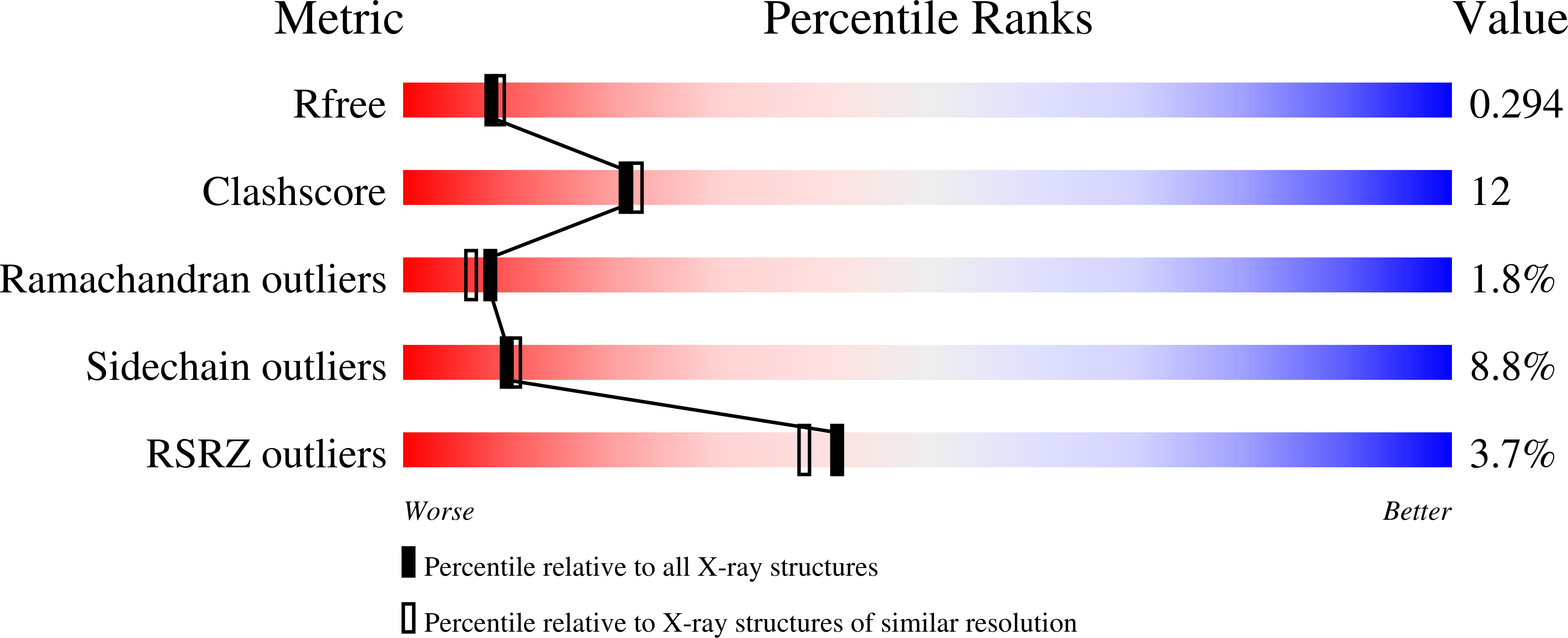
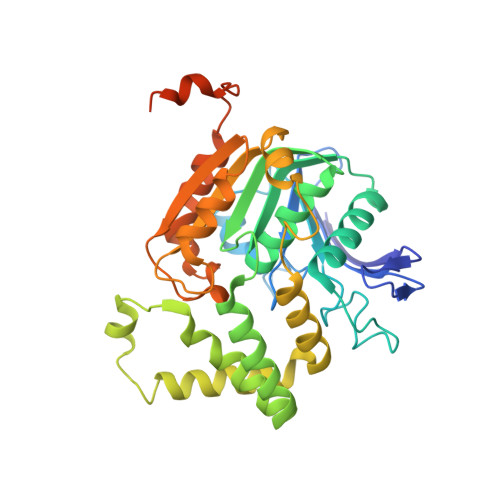
Structure of homoserine O-acetyltransferase from Staphylococcus aureus: the first Gram-positive ortholog structure.
Thangavelu, B., Pavlovsky, A.G., Viola, R.(2014) Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 70: 1340-1345
- PubMed: 25286936
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053230X14018664
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4QLO - PubMed Abstract:
Homoserine O-acetyltransferase (HTA) catalyzes the formation of L-O-acetyl-homoserine from L-homoserine through the transfer of an acetyl group from acetyl-CoA. This is the first committed step required for the biosynthesis of methionine in many fungi, Gram-positive bacteria and some Gram-negative bacteria. The structure of HTA from Staphylococcus aureus (SaHTA) has been determined to a resolution of 2.45 Å. The structure belongs to the α/β-hydrolase superfamily, consisting of two distinct domains: a core α/β-domain containing the catalytic site and a lid domain assembled into a helical bundle. The active site consists of a classical catalytic triad located at the end of a deep tunnel. Structure analysis revealed some important differences for SaHTA compared with the few known structures of HTA.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, The University of Toledo, Toledo, OH 43606, USA.