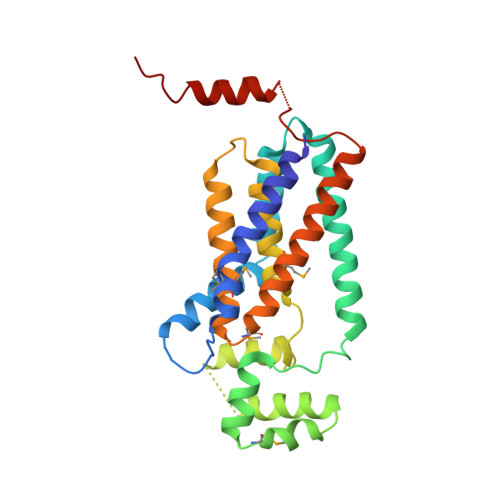
Crystal structure of lipid phosphatase Escherichia coli phosphatidylglycerophosphate phosphatase B.
Fan, J., Jiang, D., Zhao, Y., Liu, J., Zhang, X.C.(2014) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111: 7636-7640
- PubMed: 24821770
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1403097111
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4PX7 - PubMed Abstract:
Membrane-integrated type II phosphatidic acid phosphatases (PAP2s) are important for numerous bacterial to human biological processes, including glucose transport, lipid metabolism, and signaling. Escherichia coli phosphatidylglycerol-phosphate phosphatase B (ecPgpB) catalyzes removing the terminal phosphate group from a lipid carrier, undecaprenyl pyrophosphate, and is essential for transport of many hydrophilic small molecules across the membrane. We determined the crystal structure of ecPgpB at a resolution of 3.2 Å. This structure shares a similar folding topology and a nearly identical active site with soluble PAP2 enzymes. However, the substrate binding mechanism appears to be fundamentally different from that in soluble PAP2 enzymes. In ecPgpB, the potential substrate entrance to the active site is located in a cleft formed by a V-shaped transmembrane helix pair, allowing lateral movement of the lipid substrate entering the active site from the membrane lipid bilayer. Activity assays of point mutations confirmed the importance of the catalytic residues and potential residues involved in phosphate binding. The structure also suggests an induced-fit mechanism for the substrate binding. The 3D structure of ecPgpB serves as a prototype to study eukaryotic PAP2 enzymes, including human glucose-6-phosphatase, a key enzyme in the homeostatic regulation of blood glucose concentrations.
- National Laboratory of Macromolecules, National Center of Protein Science-Beijing, Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China;Graduate School of the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China;
Organizational Affiliation: