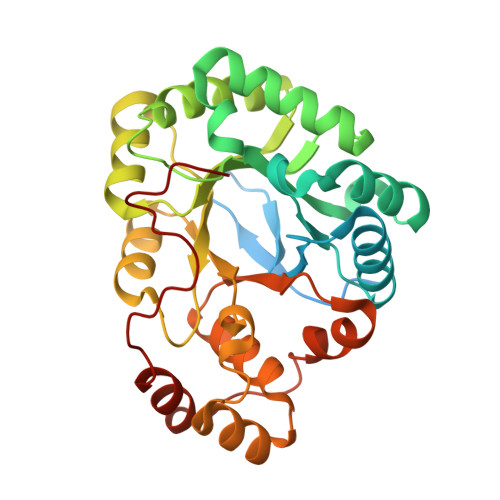
A structural characterization of the isoniazid Mycobacterium tuberculosis drug target, Rv2971, in its unliganded form
Shahine, A., Prasetyoputri, A., Rossjohn, J., Beddoe, T.(2014) Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 70: 572-577
- PubMed: 24817712
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053230X14007158
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4OTK - PubMed Abstract:
Aldo-keto reductases (AKR) are a large superfamily of NADPH-dependent oxidoreductases and play a role in detoxification of toxic metabolites. Rv2971, an AKR in Mycobacterium tuberculosis, has recently been identified as a target of isoniazid, a key first-line drug against tuberculosis. Here, the cloning, expression, purification, crystallization and structural characterization of Rv2971 are described. To gain insight into its function, the crystal structure of Rv2971 was successfully determined to 1.60 Å resolution in its unliganded form. The structure exhibits a TIM-barrel fold typical of AKRs, revealing structural characteristics essential for function and substrate specificities, allowing a structural comparison between Rv2971 and other mycobacterial AKRs.
- Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Monash University, Clayton, Victoria, Australia.
Organizational Affiliation: