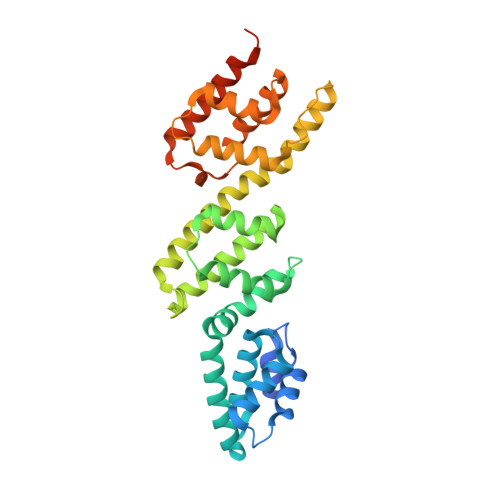
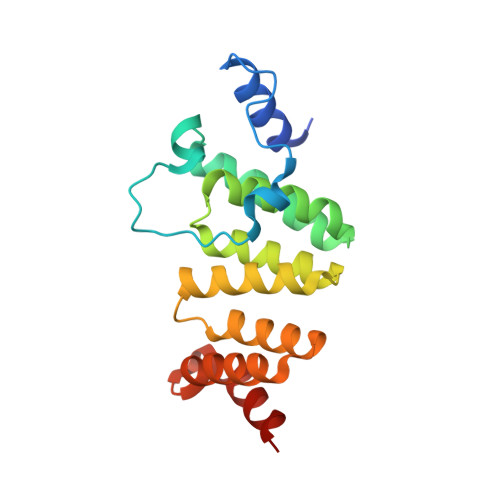
A gatekeeper chaperone complex directs translocator secretion during type three secretion.
Archuleta, T.L., Spiller, B.W.(2014) PLoS Pathog 10: e1004498-e1004498
- PubMed: 25375170
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1004498
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4NRH - PubMed Abstract:
Many Gram-negative bacteria use Type Three Secretion Systems (T3SS) to deliver effector proteins into host cells. These protein delivery machines are composed of cytosolic components that recognize substrates and generate the force needed for translocation, the secretion conduit, formed by a needle complex and associated membrane spanning basal body, and translocators that form the pore in the target cell. A defined order of secretion in which needle component proteins are secreted first, followed by translocators, and finally effectors, is necessary for this system to be effective. While the secreted effectors vary significantly between organisms, the ∼20 individual protein components that form the T3SS are conserved in many pathogenic bacteria. One such conserved protein, referred to as either a plug or gatekeeper, is necessary to prevent unregulated effector release and to allow efficient translocator secretion. The mechanism by which translocator secretion is promoted while effector release is inhibited by gatekeepers is unknown. We present the structure of the Chlamydial gatekeeper, CopN, bound to a translocator-specific chaperone. The structure identifies a previously unknown interface between gatekeepers and translocator chaperones and reveals that in the gatekeeper-chaperone complex the canonical translocator-binding groove is free to bind translocators. Structure-based mutagenesis of the homologous complex in Shigella reveals that the gatekeeper-chaperone-translocator complex is essential for translocator secretion and for the ordered secretion of translocators prior to effectors.
- Chemical and Physical Biology Program, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, Tennessee, United States of America.
Organizational Affiliation: