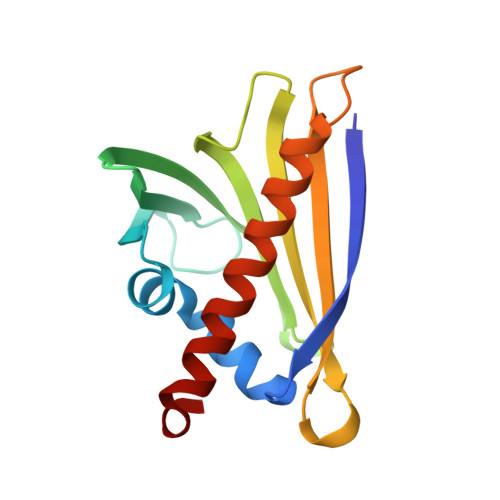
Structure and Function of the Peanut Panallergen Ara h 8.
Hurlburt, B.K., Offermann, L.R., McBride, J.K., Majorek, K.A., Maleki, S.J., Chruszcz, M.(2013) J Biological Chem 288: 36890-36901
- PubMed: 24253038
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.517797
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4M9B, 4M9W, 4MA6, 4MAP - PubMed Abstract:
The incidence of peanut allergy continues to rise in the United States and Europe. Whereas exposure to the major allergens Ara h 1, 2, 3, and 6 can cause fatal anaphylaxis, exposure to the minor allergens usually does not. Ara h 8 is a minor allergen. Importantly, it is the minor food allergens that are thought to be responsible for oral allergy syndrome (OAS), in which sensitization to airborne allergens causes a Type 2 allergic reaction to ingested foods. Furthermore, it is believed that similar protein structure rather than a similar linear sequence is the cause of OAS. Bet v 1 from birch pollen is a common sensitizing agent, and OAS results when patients consume certain fruits, vegetables, tree nuts, and peanuts. Here, we report the three-dimensional structure of Ara h 8, a Bet v 1 homolog. The overall fold is very similar to that of Bet v 1, Api g 1 (celery), Gly m 4 (soy), and Pru av 1 (cherry). Ara h 8 binds the isoflavones quercetin and apigenin as well as resveratrol avidly.
- From the Southern Regional Research Center, Agricultural Research Service, United States Department of Agriculture, New Orleans, Louisiana 70124.
Organizational Affiliation: