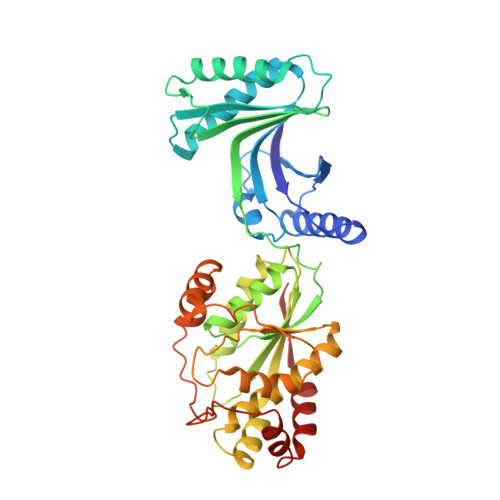
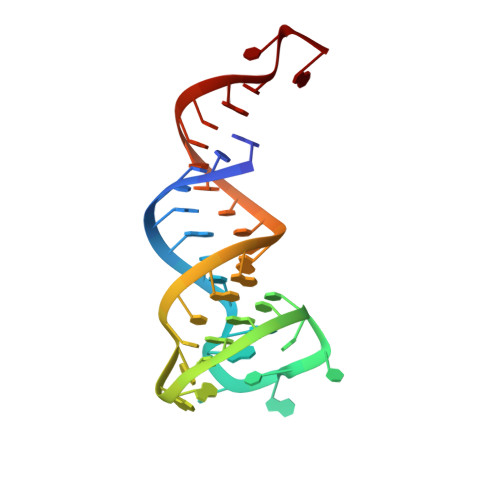
Crystal structure of a 4-thiouridine synthetase-RNA complex reveals specificity of tRNA U8 modification.
Neumann, P., Lakomek, K., Naumann, P.T., Erwin, W.M., Lauhon, C.T., Ficner, R.(2014) Nucleic Acids Res 42: 6673-6685
- PubMed: 24705700
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku249
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4KR6, 4KR7, 4KR9 - PubMed Abstract:
In prokaryotes and archaea transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA) stability as well as cellular UV protection relies on the post-transcriptional modification of uracil at position 8 (U8) of tRNAs by the 4-thiouridine synthetase ThiI. Here, we report three crystal structures of ThiI from Thermotoga maritima in complex with a truncated tRNA. The RNA is mainly bound by the N-terminal ferredoxin-like domain (NFLD) and the THUMP domain of one subunit within the ThiI homo-dimer thereby positioning the U8 close to the catalytic center in the pyrophosphatase domain of the other subunit. The recognition of the 3'-CCA end by the THUMP domain yields a molecular ruler defining the specificity for U8 thiolation. This first structure of a THUMP/NFLD-RNA complex might serve as paradigm for the RNA recognition by THUMP domains of other proteins. The ternary ThiI-RNA-ATP complex shows no significant structural changes due to adenosine triphosphate (ATP) binding, but two different states of active site loops are observed independent of the nucleotide loading state. Thereby conformational changes of the active site are coupled with conformational changes of the bound RNA. The ThiI-RNA complex structures indicate that full-length tRNA has to adopt a non-canonical conformation upon binding to ThiI.
- Department of Molecular Structural Biology, Institute of Microbiology and Genetics, GZMB, University of Göttingen, 37077 Göttingen, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: