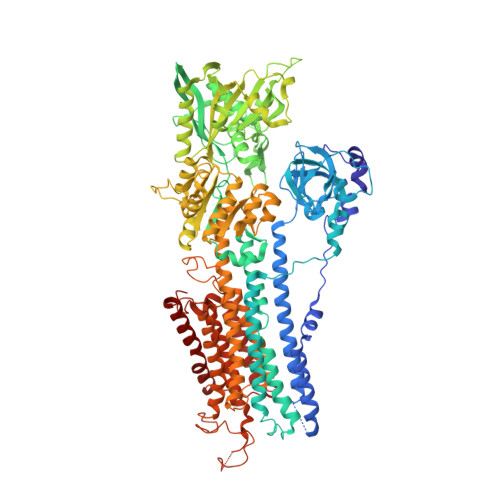
The sarcolipin-bound calcium pump stabilizes calcium sites exposed to the cytoplasm.
Winther, A.M., Bublitz, M., Karlsen, J.L., Moller, J.V., Hansen, J.B., Nissen, P., Buch-Pedersen, M.J.(2013) Nature 495: 265-269
- PubMed: 23455424
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11900
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4H1W - PubMed Abstract:
The contraction and relaxation of muscle cells is controlled by the successive rise and fall of cytosolic Ca(2+), initiated by the release of Ca(2+) from the sarcoplasmic reticulum and terminated by re-sequestration of Ca(2+) into the sarcoplasmic reticulum as the main mechanism of Ca(2+) removal. Re-sequestration requires active transport and is catalysed by the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase (SERCA), which has a key role in defining the contractile properties of skeletal and heart muscle tissue. The activity of SERCA is regulated by two small, homologous membrane proteins called phospholamban (PLB, also known as PLN) and sarcolipin (SLN). Detailed structural information explaining this regulatory mechanism has been lacking, and the structural features defining the pathway through which cytoplasmic Ca(2+) enters the intramembranous binding sites of SERCA have remained unknown. Here we report the crystal structure of rabbit SERCA1a (also known as ATP2A1) in complex with SLN at 3.1 Å resolution. The regulatory SLN traps the Ca(2+)-ATPase in a previously undescribed E1 state, with exposure of the Ca(2+) sites through an open cytoplasmic pathway stabilized by Mg(2+). The structure suggests a mechanism for selective Ca(2+) loading and activation of SERCA, and provides new insight into how SLN and PLB inhibition arises from stabilization of this E1 intermediate state without bound Ca(2+). These findings may prove useful in studying how autoinhibitory domains of other ion pumps modulate transport across biological membranes.
- Pcovery, Thorvaldsensvej 57, DK-1871 Frederiksberg, Denmark.
Organizational Affiliation: