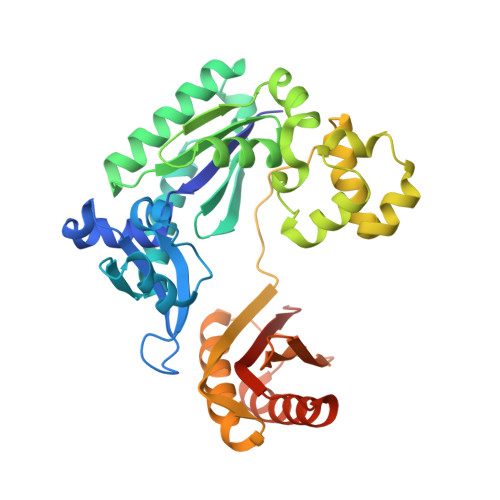
Differential furanose selection in the active sites of archaeal DNA polymerases probed by fixed-conformation nucleotide analogues.
Ketkar, A., Zafar, M.K., Banerjee, S., Marquez, V.E., Egli, M., Eoff, R.L.(2012) Biochemistry 51: 9234-9244
- PubMed: 23050956
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi301043k
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4GC6, 4GC7 - PubMed Abstract:
DNA polymerases select for the incorporation of deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs) using amino acid side-chains that act as a "steric-gate" to bar improper incorporation of rNTPs. An additional factor in the selection of nucleotide substrates resides in the preferred geometry for the furanose moiety of the incoming nucleotide triphosphate. We have probed the role of sugar geometry during nucleotide selection by model DNA polymerases from Sulfolobus solfataricus using fixed conformation nucleotide analogues. North-methanocarba-dATP (N-MC-dATP) locks the central ring into a RNA-type (C2'-exo, North) conformation near a C3'-endo pucker, and South-methanocarba-dATP (S-MC-dATP) locks the central ring system into a (C3'-exo, South) conformation near a C2'-endo pucker. Dpo4 preferentially inserts N-MC-dATP and in the crystal structure of Dpo4 in complex with N-MC-dAMP, the nucleotide analogue superimposes almost perfectly with Dpo4 bound to unmodified dATP. Biochemical assays indicate that the S. solfataricus B-family DNA polymerase Dpo1 can insert and extend from both N-MC-dATP and S-MC-dATP. In this respect, Dpo1 is unexpectedly more tolerant of substrate conformation than Dpo4. The crystal structure of Dpo4 bound to S-MC-dADP shows that poor incorporation of the Southern pucker by the Y-family polymerase results from a hydrogen bond between the 3'-OH group of the nucleotide analogue and the OH group of the steric gate residue, Tyr12, shifting the S-MC-dADP molecule away from the dNTP binding pocket and distorting the base pair at the primer-template junction. These results provide insights into substrate specificity of DNA polymerases, as well as molecular mechanisms that act as a barrier against insertion of rNTPs.
- Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, Arkansas 72205-7199, United States.
Organizational Affiliation: