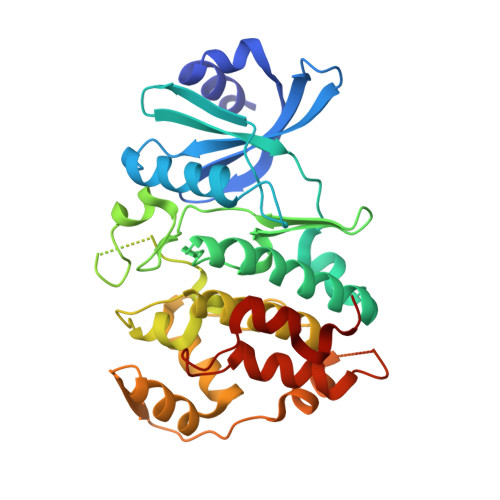
Crystal structure of human CDC7 kinase in complex with its activator DBF4.
Hughes, S., Elustondo, F., Di Fonzo, A., Leroux, F.G., Wong, A.C., Snijders, A.P., Matthews, S.J., Cherepanov, P.(2012) Nat Struct Mol Biol 19: 1101-1107
- PubMed: 23064647
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2404
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4F99, 4F9A, 4F9B, 4F9C - PubMed Abstract:
CDC7 is a serine/threonine kinase that is essential for the initiation of eukaryotic DNA replication. CDC7 activity is controlled by its activator, DBF4. Here we present crystal structures of human CDC7-DBF4 in complex with a nucleotide or ATP-competing small molecules, revealing the active and inhibited forms of the kinase, respectively. DBF4 wraps around CDC7, burying approximately 6,000 Å(2) of hydrophobic molecular surface in a bipartite interface. The effector domain of DBF4, containing conserved motif C, is essential and sufficient to support CDC7 kinase activity by binding to the kinase N-terminal lobe and stabilizing its canonical αC helix. DBF4 motif M latches onto the C-terminal lobe of the kinase, acting as a tethering domain. Our results elucidate the structural basis for binding to and activation of CDC7 by DBF4 and provide a framework for the design of more potent and specific CDC7 inhibitors.
- Cancer Research UK, London Research Institute, Clare Hall Laboratories, Potters Bar, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: