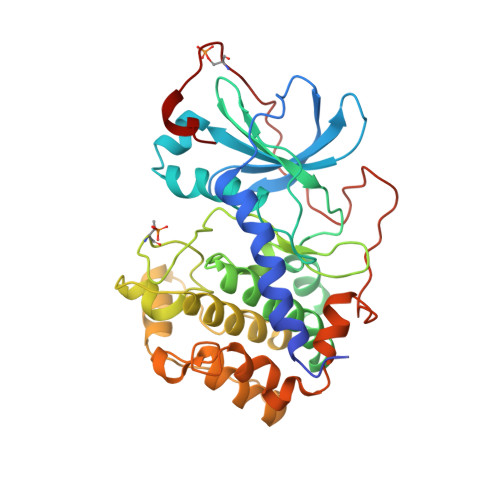
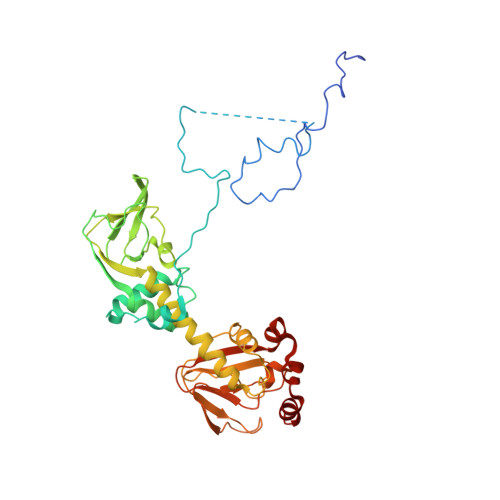
Localization and quaternary structure of the PKA RI Beta holoenzyme
Ilouz, R., Bubis, J., Wu, J., Yim, Y.Y., Deal, M.S., Kornev, A.P., Ma, Y., Blumenthal, D.K., Taylor, S.S.(2012) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109: 12443-12448
- PubMed: 22797896
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1209538109
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4DIN - PubMed Abstract:
Specificity for signaling by cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) is achieved by both targeting and isoform diversity. The inactive PKA holoenzyme has two catalytic (C) subunits and a regulatory (R) subunit dimer (R(2):C(2)). Although the RIα, RIIα, and RIIβ isoforms are well studied, little is known about RIβ. We show here that RIβ is enriched selectively in mitochondria and hypothesized that its unique biological importance and functional nonredundancy will correlate with its structure. Small-angle X-ray scattering showed that the overall shape of RIβ(2):C(2) is different from its closest homolog, RIα(2):C(2). The full-length RIβ(2):C(2) crystal structure allows us to visualize all the domains of the PKA holoenzyme complex and shows how isoform-specific assembly of holoenzyme complexes can create distinct quaternary structures even though the R(1):C(1) heterodimers are similar in all isoforms. The creation of discrete isoform-specific PKA holoenzyme signaling "foci" paves the way for exploring further biological roles of PKA RIβ and establishes a paradigm for PKA signaling.
- Howard Hughes Medical Institute, and Departments of Chemistry and Biochemistry and Pharmacology, University of California at San Diego, La Jolla, CA 92093, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: