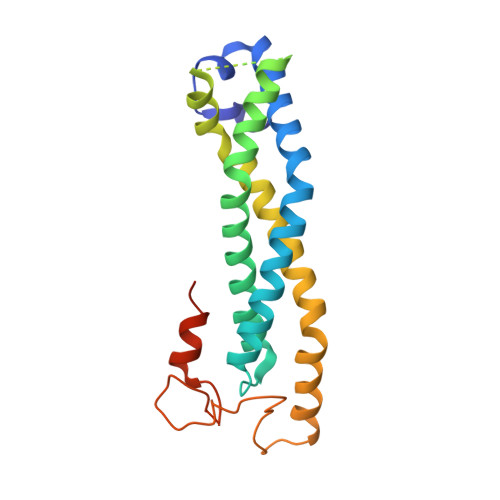
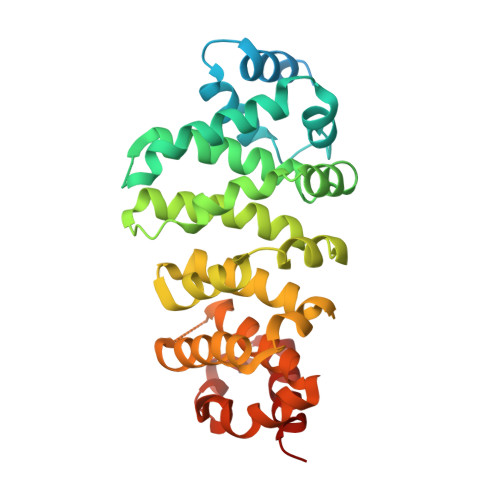
Structural and Biochemical Insights to the Role of the Ccr4-not Complex and Ddx6 ATPase in Microrna Repression.
Mathys, H., Basquin, J., Ozgur, S., Czarnocki-Cieciura, M., Bonneau, F., Aartse, A., Dziembowski, A., Nowotny, M., Conti, E., Filipowicz, W.(2014) Mol Cell 54: 751
- PubMed: 24768538
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2014.03.036
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4CT4, 4CT5, 4CT6, 4CT7, 4CV5 - PubMed Abstract:
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) control gene expression by regulating mRNA translation and stability. The CCR4-NOT complex is a key effector of miRNA function acting downstream of GW182/TNRC6 proteins. We show that miRNA-mediated repression requires the central region of CNOT1, the scaffold protein of CCR4-NOT. A CNOT1 domain interacts with CNOT9, which in turn interacts with the silencing domain of TNRC6 in a tryptophan motif-dependent manner. These interactions are direct, as shown by the structure of a CNOT9-CNOT1 complex with bound tryptophan. Another domain of CNOT1 with an MIF4G fold recruits the DEAD-box ATPase DDX6, a known translational inhibitor. Structural and biochemical approaches revealed that CNOT1 modulates the conformation of DDX6 and stimulates ATPase activity. Structure-based mutations showed that the CNOT1 MIF4G-DDX6 interaction is important for miRNA-mediated repression. These findings provide insights into the repressive steps downstream of the GW182/TNRC6 proteins and the role of the CCR4-NOT complex in posttranscriptional regulation in general.
- Friedrich Miescher Institute for Biomedical Research, 4058 Basel, Switzerland; University of Basel, 4003 Basel, Switzerland.
Organizational Affiliation: