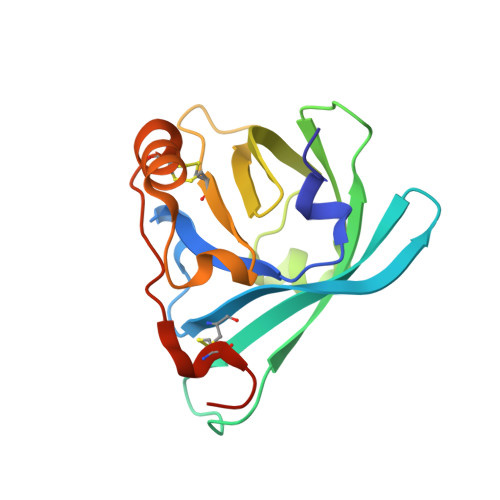
Structural basis of cholesterol binding by a novel clade of dendritic cell modulators from ticks.
Roversi, P., Johnson, S., Preston, S.G., Nunn, M.A., Paesen, G.C., Austyn, J.M., Nuttall, P.A., Lea, S.M.(2017) Sci Rep 7: 16057-16057
- PubMed: 29167574
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-16413-2
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4BOE, 4BQU - PubMed Abstract:
Two crystal structures of Japanin, an 18 kDa immune-modulatory lipocalin from the Brown Ear Tick (Rhipicephalus appendiculatus), have been determined at 2.2 and 2.4 Å resolution. In both crystal forms the protein is in complex with cholesterol, which sits in a closed pocket at the centre of the lipocalin barrel. Both crystal forms are dimers, which are also observed in solution. Molecular modelling suggests that previously-described members of a tick protein family bearing high sequence homology to Japanin are also likely to bind cholesterol or cholesterol derivatives.
- Biochemistry Department, University of Oxford, Oxford, OX1 3QU, England, United Kingdom. pietro.roversi@bioch.ox.ac.uk.
Organizational Affiliation: