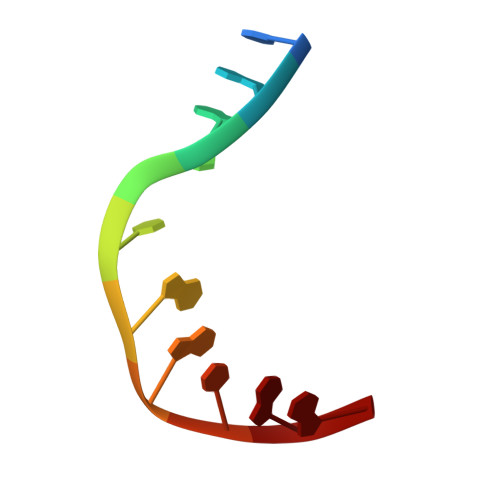
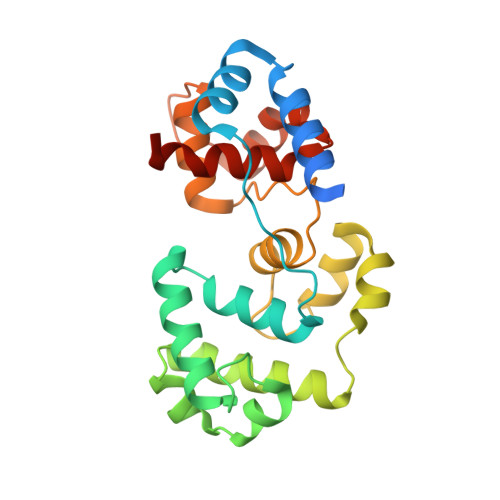
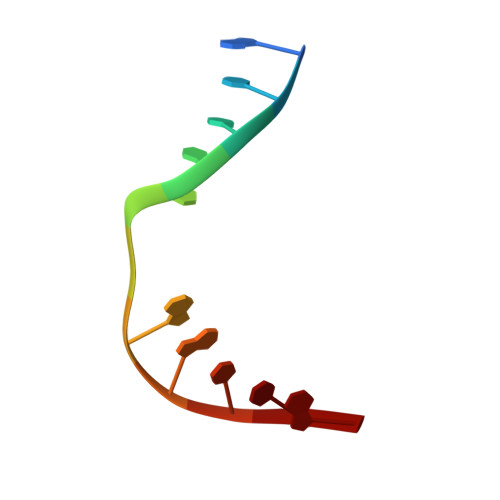
Sculpting of DNA at Abasic Sites by DNA Glycosylase Homolog Mag2.
Dalhus, B., Nilsen, L., Korvald, H., Huffman, J., Forstrom, R.J., Mcmurray, C.T., Alseth, I., Tainer, J.A., Bjoras, M.(2013) Structure 21: 154
- PubMed: 23245849
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2012.11.004
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4B21, 4B22, 4B23, 4B24 - PubMed Abstract:
Modifications and loss of bases are frequent types of DNA lesions, often handled by the base excision repair (BER) pathway. BER is initiated by DNA glycosylases, generating abasic (AP) sites that are subsequently cleaved by AP endonucleases, which further pass on nicked DNA to downstream DNA polymerases and ligases. The coordinated handover of cytotoxic intermediates between different BER enzymes is most likely facilitated by the DNA conformation. Here, we present the atomic structure of Schizosaccharomyces pombe Mag2 in complex with DNA to reveal an unexpected structural basis for nonenzymatic AP site recognition with an unflipped AP site. Two surface-exposed loops intercalate and widen the DNA minor groove to generate a DNA conformation previously only found in the mismatch repair MutS-DNA complex. Consequently, the molecular role of Mag2 appears to be AP site recognition and protection, while possibly facilitating damage signaling by structurally sculpting the DNA substrate.
- Department of Microbiology, Centre of Molecular Biology and Neuroscience, Oslo University Hospital, Rikshospitalet, PO Box 4950, Nydalen, N-0424, Oslo, Norway; Department of Medical Biochemistry, Oslo University Hospital, Rikshospitalet, PO Box 4950, Nydalen, N-0424, Oslo, Norway.
Organizational Affiliation: