Combinatorial readout of unmodified H3R2 and acetylated H3K14 by the tandem PHD finger of MOZ reveals a regulatory mechanism for HOXA9 transcription
Qiu, Y., Liu, L., Zhao, C., Han, C., Li, F., Zhang, J., Wang, Y., Li, G., Mei, Y., Wu, M., Wu, J., Shi, Y.(2012) Genes Dev 26: 1376-1391
- PubMed: 22713874
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.188359.112
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2LN0, 3V43 - PubMed Abstract:
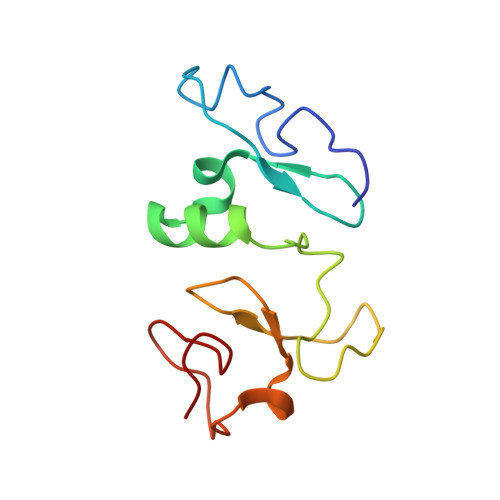
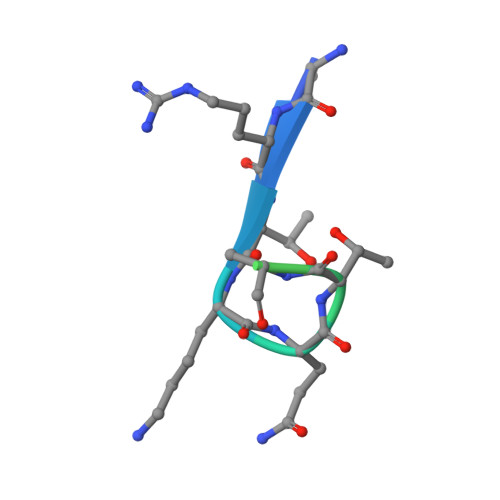
Histone acetylation is a hallmark for gene transcription. As a histone acetyltransferase, MOZ (monocytic leukemia zinc finger protein) is important for HOX gene expression as well as embryo and postnatal development. In vivo, MOZ forms a tetrameric complex with other subunits, including several chromatin-binding modules with regulatory functions. Here we report the solution structure of the tandem PHD (plant homeodomain) finger (PHD12) of human MOZ in a free state and the 1.47 Å crystal structure in complex with H3K14ac peptide, which reveals the structural basis for the recognition of unmodified R2 and acetylated K14 on histone H3. Moreover, the results of chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) and RT-PCR assays indicate that PHD12 facilitates the localization of MOZ onto the promoter locus of the HOXA9 gene, thereby promoting the H3 acetylation around the promoter region and further up-regulating the HOXA9 mRNA level. Taken together, our findings suggest that the combinatorial readout of the H3R2/K14ac by PHD12 might represent an important epigenetic regulatory mechanism that governs transcription and also provide a clue of cross-talk between the MOZ complex and histone H3 modifications.
- Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui 230026, China.
Organizational Affiliation: