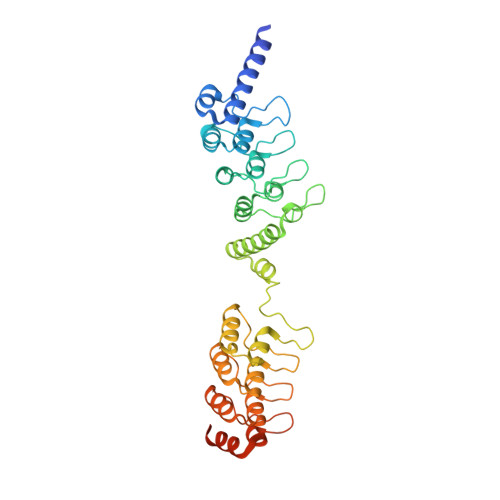
Crystal structure of a Tankyrase-Axin complex and its implications for Axin turnover and Tankyrase substrate recruitment.
Morrone, S., Cheng, Z., Moon, R.T., Cong, F., Xu, W.(2012) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109: 1500-1505
- PubMed: 22307604
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1116618109
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3UTM - PubMed Abstract:
Axin is a tumor suppressor and a key negative regulator of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Axin turnover is controlled by its poly-ADP-ribosylation catalyzed by tankyrase (TNKS), which requires the direct interaction of Axin with TNKS. This interaction is thus an attractive drug target for treating cancers, brain injuries, and other diseases where β-catenin is involved. Here we report the crystal structure of a mouse TNKS1 fragment containing ankyrin-repeat clusters 2 and 3 (ARC2-3) in a complex with the TNKS-binding domain of mouse Axin1. Surprisingly, we found that Axin contains two discrete TNKS-binding segments, both of which bind simultaneously to the two ARC2 domains in the ARC2-3 homodimer. Our crystal structure shows that in each TNKS-binding segment of Axin there is a conserved glycine residue that lies in the bottom of a narrow "gate" formed by two parallel tyrosine side chains on the TNKS surface. This glycine-selection gate is crucial for TNKS-Axin interactions, as mutation of the TNKS gate-forming residues, or mutation of either glycine residue in the two Axin segments, completely abolishes the binding of the corresponding Axin segment to TNKS. The bivalent binding of Axin to TNKS is required for Axin turnover, since mutations in either gate-binding glycine residue in Axin lead to Axin stabilization in the cell. In addition, our analyses also reveal the structural basis for TNKS substrate recruitment, and shed light on the overall structure of TNKS that should help in developing specific inhibitors of Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
- Department of Biological Structure, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA 98195, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: