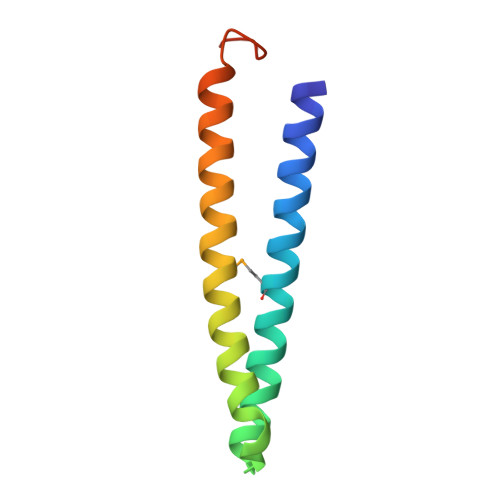
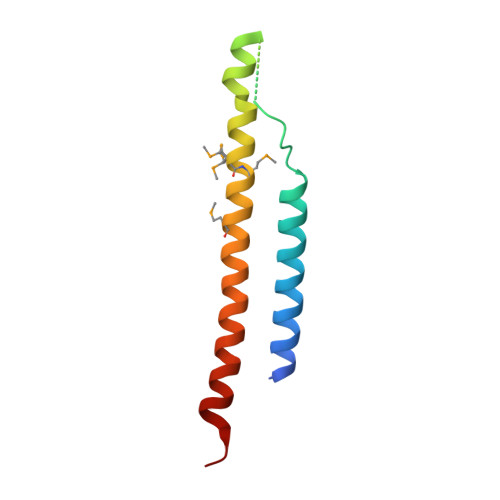
Mediator head subcomplex Med11/22 contains a common helix bundle building block with a specific function in transcription initiation complex stabilization.
Seizl, M., Lariviere, L., Pfaffeneder, T., Wenzeck, L., Cramer, P.(2011) Nucleic Acids Res 39: 6291-6304
- PubMed: 21498544
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr229
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3R84 - PubMed Abstract:
Mediator is a multiprotein co-activator of RNA polymerase (Pol) II transcription. Mediator contains a conserved core that comprises the 'head' and 'middle' modules. We present here a structure-function analysis of the essential Med11/22 heterodimer, a part of the head module. Med11/22 forms a conserved four-helix bundle domain with C-terminal extensions, which bind the central head subunit Med17. A highly conserved patch on the bundle surface is required for stable transcription pre-initiation complex formation on a Pol II promoter in vitro and in vivo and may recruit the general transcription factor TFIIH. The bundle domain fold is also present in the Mediator middle module subcomplex Med7/21 and is predicted in the Mediator heterodimers Med2/3, Med4/9, Med10/14 and Med28/30. The bundle domain thus represents a common building block that has been multiplied and functionally diversified during Mediator evolution in eukaryotes.
- Gene Center and Department of Biochemistry, Center for Integrated Protein Science Munich, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, Feodor-Lynen-Strasse 25, 81377 Munich, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: