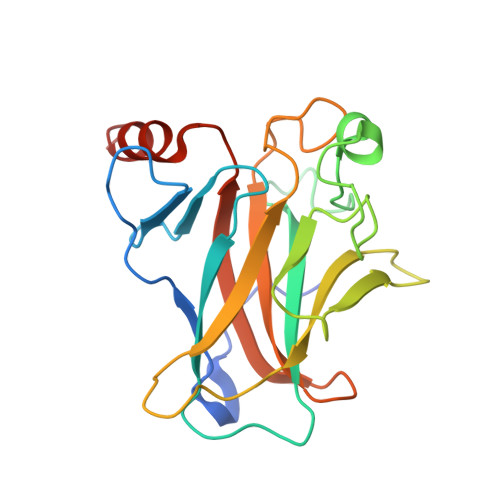
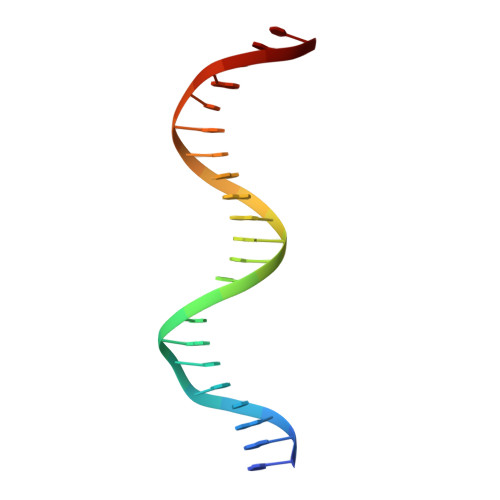
Structures of p63 DNA binding domain in complexes with half-site and with spacer-containing full response elements.
Chen, C., Gorlatova, N., Kelman, Z., Herzberg, O.(2011) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108: 6456-6461
- PubMed: 21464285
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1013657108
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3QYM, 3QYN - PubMed Abstract:
Transcription factor p63, a p53 family member, plays a role in epithelial cell development, cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, and tumorigenesis. Point mutations, primarily in the DNA binding domain (p63DBD), lead to malformation syndromes. To gain insight into differences between p63 and p53 and the impact of mutations on the structure, we have determined two crystal structures of p63DBD in complex with A/T-rich response elements. One complex contains a 10-bp DNA half-site response element (5'AAACATGTTT3') and the other contains a 22-bp DNA full response element with a 2-bp spacer between two half-sites (5'AAACATGTTTTAAAACATGTTT3'). In both structures, each half-site binds a p63DBD dimer. The two p63DBD dimers do not interact in the presence of the DNA spacer, whereas they interact with one another in the p63DBD/10-bp complex where the DNA simulates a full response element by packing end-to-end. A unique dimer-dimer interaction involves a variable loop region, which differs in length and sequence from the counterpart loop of p53DBD. The DNA trajectories in both structures assume superhelical conformations. Surface plasmon resonance studies of p63DBD/DNA binding yielded K(d) = 11.7 μM for a continuous full response element, whereas binding was undetectable with the 22-bp DNA, suggesting an important contribution of a p63DBD interdimer interface to binding and establishing that p63DBD affinity to the response element is approximately 1,000-fold lower than that of p53DBD. Analyses of the structural consequences of p63DBD mutations that cause developmental defects show that, although some mutations affect DNA binding directly, the majority affects protein stability.
- William Myron Keck Laboratory for Structural Biology, Institute for Bioscience and Biotechnology Research, University of Maryland, Rockville, MD 20850, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: