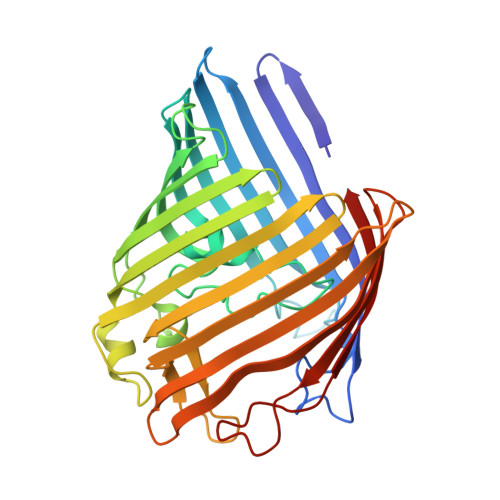
Structure of Escherichia coli OmpF porin from lipidic mesophase.
Efremov, R.G., Sazanov, L.A.(2012) J Struct Biol 178: 311-318
- PubMed: 22484237
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsb.2012.03.005
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3POQ, 3POU, 3POX - PubMed Abstract:
Outer membrane protein F, a major component of the Escherichia coli outer membrane, was crystallized for the first time in lipidic mesophase of monoolein in novel space groups, P1 and H32. Due to ease of its purification and crystallization OmpF can be used as a benchmark protein for establishing membrane protein crystallization in meso, as a "membrane lyzozyme". The packing of porin trimers in the crystals of space group H32 is similar to natural outer membranes, providing the first high-resolution insight into the close to native packing of OmpF. Surprisingly, interaction between trimers is mediated exclusively by lipids, without direct protein-protein contacts. Multiple ordered lipids are observed and many of them occupy identical positions independently of the space group, identifying preferential interaction sites of lipid acyl chains. Presence of ordered aliphatic chains close to a positively charged area on the porin surface suggests a position for a lipopolysaccharide binding site on the surface of the major E. coli porins.
- Medical Research Council Mitochondrial Biology Unit, Wellcome Trust/MRC Building, Hills Road, Cambridge CB2 0XY, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: