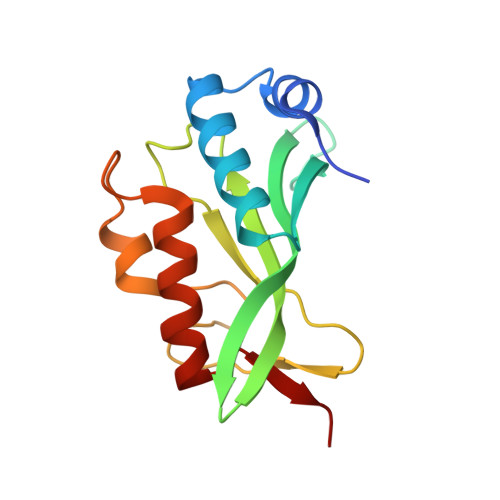
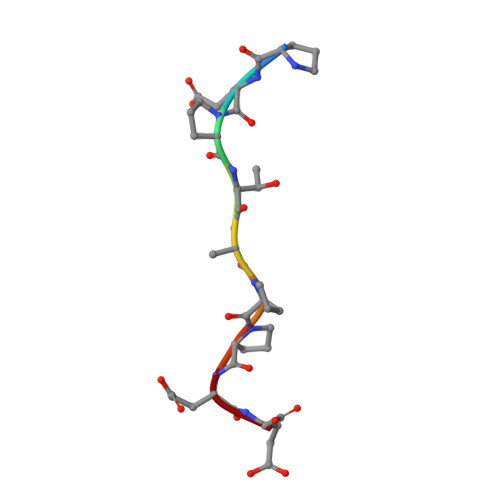
Crystallographic and Functional Analysis of the ESCRT-I /HIV-1 Gag PTAP Interaction.
Im, Y.J., Kuo, L., Ren, X., Burgos, P.V., Zhao, X.Z., Liu, F., Burke, T.R., Bonifacino, J.S., Freed, E.O., Hurley, J.H.(2010) Structure 18: 1536-1547
- PubMed: 21070952
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2010.08.010
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3OBQ, 3OBS, 3OBU, 3OBX - PubMed Abstract:
Budding of HIV-1 requires the binding of the PTAP late domain of the Gag p6 protein to the UEV domain of the TSG101 subunit of ESCRT-I. The normal function of this motif in cells is in receptor downregulation. Here, we report the 1.4-1.6 Å structures of the human TSG101 UEV domain alone and with wild-type and mutant HIV-1 PTAP and Hrs PSAP nonapeptides. The hydroxyl of the Thr or Ser residue in the P(S/T)AP motif hydrogen bonds with the main chain of Asn69. Mutation of the Asn to Pro, blocking the main-chain amide, abrogates PTAP motif binding in vitro and blocks budding of HIV-1 from cells. N69P and other PTAP binding-deficient alleles of TSG101 did not rescue HIV-1 budding. However, the mutant alleles did rescue downregulation of endogenous EGF receptor. This demonstrates that the PSAP motif is not rate determining in EGF receptor downregulation under normal conditions.
- Laboratory of Molecular Biology, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD 20892-0580, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: