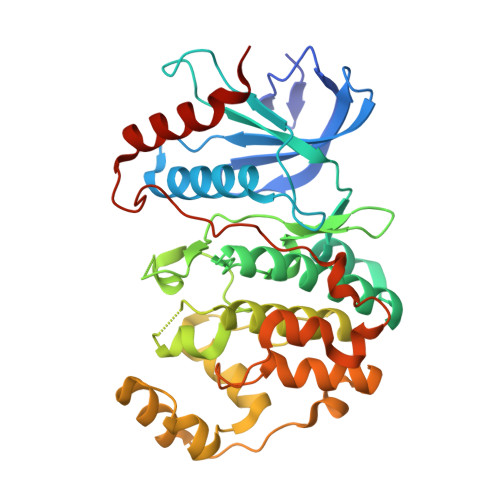
Phosphorylation of DCC by ERK2 is facilitated by direct docking of the receptor P1 domain to the kinase
Ma, W., Shang, Y., Wei, Z., Wen, W., Wang, W., Zhang, M.(2010) Structure 18: 1502-1511
- PubMed: 21070949
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2010.08.011
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3O71 - PubMed Abstract:
Netrin receptor DCC plays critical roles in many cellular processes, including axonal outgrowth and migration, angiogenesis, and apoptosis, but the molecular basis of DCC-mediated signaling is largely unclear. ERK2, a member of the MAPK family, is one of the few proteins known to be involved in DCC-mediated signaling. Here, we report that ERK2 directly interacts with DCC, and the ERK2-binding region was mapped to the conserved intracellular P1 domain of the receptor. The structure of ERK2 in complex with the P1 domain of DCC reveals that DCC contains a MAPK docking motif. The docking of the P1 domain onto ERK2 physically positions several phosphorylation sites of DCC in the vicinity of the kinase active site. We further show that the docking interaction between the P1 domain and ERK2 is essential for the ERK2-mediated phosphorylation of DCC. We conclude that DCC signaling is directly coupled with MAPK signaling cascades.
- Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, Shanghai, P.R. China.
Organizational Affiliation: