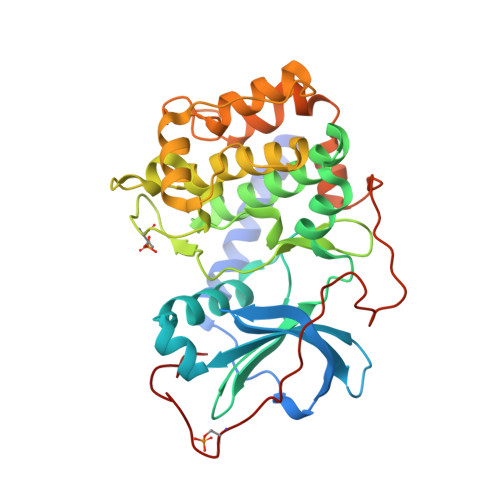
Azole-based inhibitors of AKT/PKB for the treatment of cancer.
Zeng, Q., Allen, J.G., Bourbeau, M.P., Wang, X., Yao, G., Tadesse, S., Rider, J.T., Yuan, C.C., Hong, F.T., Lee, M.R., Zhang, S., Lofgren, J.A., Freeman, D.J., Yang, S., Li, C., Tominey, E., Huang, X., Hoffman, D., Yamane, H.K., Fotsch, C., Dominguez, C., Hungate, R., Zhang, X.(2010) Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20: 1559-1564
- PubMed: 20137943
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.01.067
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3L9L, 3L9M, 3L9N - PubMed Abstract:
Through a combination of screening and structure-based rational design, we have discovered a series of N(1)-(5-(heterocyclyl)-thiazol-2-yl)-3-(4-trifluoromethylphenyl)-1,2-propanediamines that were developed into potent ATP competitive inhibitors of AKT. Studies of linker strand-binding adenine isosteres identified SAR trends in potency and selectivity that were consistent with binding interactions observed in structures of the inhibitors bound to AKT1 and to the counter-screening target PKA. One compound was shown to have acceptable pharmacokinetic properties and to be a potent inhibitor of AKT signaling and of in vivo xenograft tumor growth in a preclinical model of glioblastoma.
- Chemistry Research and Discovery, Amgen Inc., One Amgen Center Drive, Thousand Oaks, CA 91320, United States.
Organizational Affiliation: