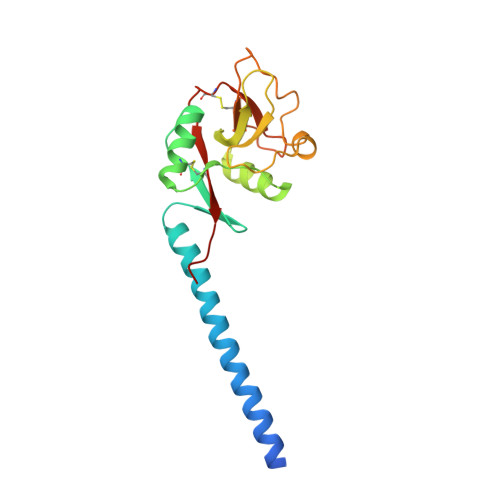
Trimeric structure of langerin.
Feinberg, H., Powlesland, A.S., Taylor, M.E., Weis, W.I.(2010) J Biological Chem 285: 13285-13293
- PubMed: 20181944
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.086058
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3KQG - PubMed Abstract:
Langerin, an endocytic receptor of Langerhans cells, binds pathogens such as human immunodeficiency virus by recognition of surface glycoconjugates and mediates their internalization into Birbeck granules. Langerin has an extracellular region consisting of a C-type carbohydrate-recognition domain (CRD) and a neck region that stabilizes formation of trimers. As in many other C-type lectins, oligomerization is required for high affinity binding to glycan ligands and is also likely to be important for determining specificity. To facilitate structural analysis of the human langerin trimer, a truncated form of the extracellular region, consisting of part of the neck and the CRD, has been characterized. Like the full-length protein, truncated langerin exists as a stable trimer in solution. Glycan array screening with the trimeric fragment shows that high mannose oligosaccharides are the best ligands for langerin. Structural analysis of the trimeric fragment of langerin confirms that the neck region forms a coiled-coil of alpha-helices. Multiple interactions between the neck region and the CRDs make the trimer a rigid unit with the three CRDs in fixed positions and the primary sugar-binding sites separated by a distance of 42 A. The fixed orientation of the sugar-binding sites in the trimer is likely to place constraints on the ligands that can be bound by langerin.
- Department of Structural Biology, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, California 94306, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: