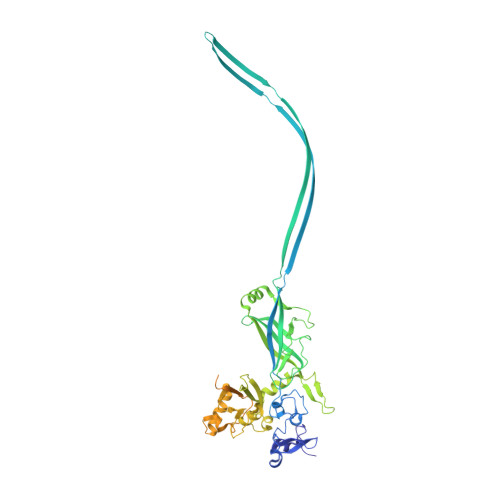
Atomic structure of anthrax protective antigen pore elucidates toxin translocation.
Jiang, J., Pentelute, B.L., Collier, R.J., Zhou, Z.H.(2015) Nature 521: 545-549
- PubMed: 25778700
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14247
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3J9C - PubMed Abstract:
Anthrax toxin, comprising protective antigen, lethal factor, and oedema factor, is the major virulence factor of Bacillus anthracis, an agent that causes high mortality in humans and animals. Protective antigen forms oligomeric prepores that undergo conversion to membrane-spanning pores by endosomal acidification, and these pores translocate the enzymes lethal factor and oedema factor into the cytosol of target cells. Protective antigen is not only a vaccine component and therapeutic target for anthrax infections but also an excellent model system for understanding the mechanism of protein translocation. On the basis of biochemical and electrophysiological results, researchers have proposed that a phi (Φ)-clamp composed of phenylalanine (Phe)427 residues of protective antigen catalyses protein translocation via a charge-state-dependent Brownian ratchet. Although atomic structures of protective antigen prepores are available, how protective antigen senses low pH, converts to active pore, and translocates lethal factor and oedema factor are not well defined without an atomic model of its pore. Here, by cryo-electron microscopy with direct electron counting, we determine the protective antigen pore structure at 2.9-Å resolution. The structure reveals the long-sought-after catalytic Φ-clamp and the membrane-spanning translocation channel, and supports the Brownian ratchet model for protein translocation. Comparisons of four structures reveal conformational changes in prepore to pore conversion that support a multi-step mechanism by which low pH is sensed and the membrane-spanning channel is formed.
- 1] Department of Microbiology, Immunology and Molecular Genetics, University of California, Los Angeles, California 90095, USA [2] California NanoSystems Institute, University of California, Los Angeles, California 90095, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: