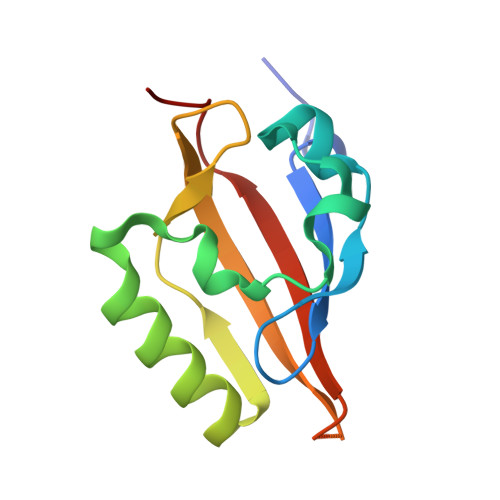
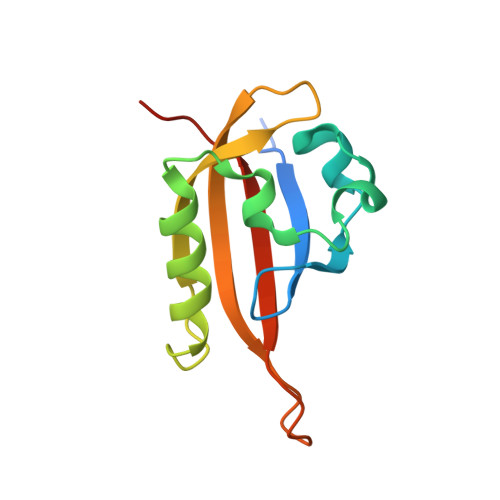
Principles of ligand binding within a completely buried cavity in HIF2alpha PAS-B
Key, J., Scheuermann, T.H., Anderson, P.C., Daggett, V., Gardner, K.H.(2009) J Am Chem Soc 131: 17647-17654
- PubMed: 19950993
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ja9073062
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3H7W, 3H82 - PubMed Abstract:
Hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) are heterodimeric transcription factors responsible for the metazoan hypoxia response and promote tumor growth, metastasis, and resistance to cancer treatment. The C-terminal Per-ARNT-Sim (PAS) domain of HIF2alpha (HIF2alpha PAS-B) contains a preformed solvent-inaccessible cavity that binds artificial ligands that allosterically perturb the formation of the HIF heterodimer. To better understand how small molecules bind within this domain, we examined the structures and equilibrium and transition-state thermodynamics of HIF2alpha PAS-B with several artificial ligands using isothermal titration calorimetry, NMR exchange spectroscopy, and X-ray crystallography. Rapid association rates reveal that ligand binding is not dependent upon a slow conformational change in the protein to permit ligand access, despite the closed conformation observed in the NMR and crystal structures. Compensating enthalpic and entropic contributions to the thermodynamic barrier for ligand binding suggest a binding-competent transition state characterized by increased structural disorder. Finally, molecular dynamics simulations reveal conversion between open and closed conformations of the protein and pathways of ligand entry into the binding pocket.
- Department of Biochemistry, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, 5323 Harry Hines Boulevard, Dallas, Texas 75390-8816, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: